03450
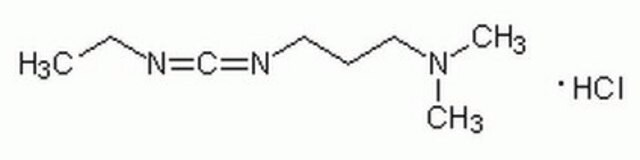
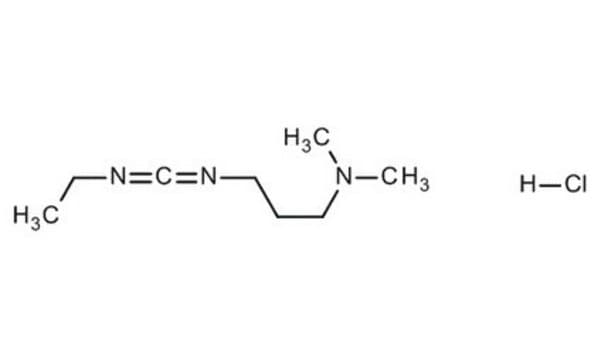
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
purum, ≥98.0% (AT)
동의어(들):
N-Ethyl-N′-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDAC, EDC, EDC hydrochloride, WSC hydrochloride
About This Item
추천 제품
grade
purum
Quality Level
분석
≥98.0% (AT)
형태
powder
mp
110-115 °C (lit.)
110-115 °C
solubility
H2O: soluble 1 gm/10 ml, clear to very slightly hazy, colorless to very faintly yellow
응용 분야
microbiology
저장 온도
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H17N3.ClH/c1-4-9-8-10-6-5-7-11(2)3;/h4-7H2,1-3H3;1H
InChI key
FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
일반 설명
The adaptability of EDAC HCl encompasses nucleic acid modification, permitting the selective labeling of DNA and RNA through their 5′ phosphate groups. This capacity contributes significantly to the visualization, tracking, and analytical aspects of these fundamental molecules, thereby advancing nucleic acid research. Furthermore, EDAC HCl functions as a biomolecule bridge, acting as a crosslinker connecting amine-reactive NHS-esters of biomolecules to carboxyl groups.
This feature proves invaluable in protein conjugation, facilitating the development of hybrid molecules with distinct properties and functions. The underlying reaction mechanism involves EDAC HCl′s interaction with a carboxyl group, forming an unstable intermediate actively seeking an amine partner. The delicate equilibrium of this reaction underscores the necessity for optimizing conditions to ensure efficient conjugation. The assistance of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) enhances the capabilities of EDAC HCl by stabilizing the intermediate and enabling two-step conjugation procedures, affording greater flexibility and control, particularly in the manipulation of complex biomolecular structures.
애플리케이션
생화학적/생리학적 작용
특징 및 장점
기타 정보
호환 제품
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
표적 기관
Stomach,large intestine,lymph node
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
이미 열람한 고객
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.