105740
α,α′-Dichloro-p-xylene
98%
Synonym(s):
1,4-Bis(chloromethyl)benzene, p-Xylylene dichloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C6H4(CH2Cl)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
175.06
Beilstein:
774706
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
form
solid
bp
254 °C (lit.)
mp
98-101 °C (lit.)
functional group
chloro
SMILES string
ClCc1ccc(CCl)cc1
InChI
1S/C8H8Cl2/c9-5-7-1-2-8(6-10)4-3-7/h1-4H,5-6H2
InChI key
ZZHIDJWUJRKHGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
α,α′-Dichloro-p-xylene undergoes phase transfer catalysed polycondensation with t-butylcyanoacetate to form carbon-carbon chain polymer.
Application
α,α′-Dichloro-p-xylene is a monomer used in preparation of poly(p-phenylene vinylene(PPV) nanotubes and nanorods by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) polymerization method. α,α′-Dichloro-p-xylene was used in a study to investigate the effect of CVD monomer selection and reaction conditions on the resulting PPV polymer layer composition and luminescence properties.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1A
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Synthesis of carbon-carbon chain polymer by phase-transfer-catalyzed polycondensation of α, α'-dichloro-p-xylene with t-butyl cyanoacetate.
Imai Y, et al.
Journal of Polymer Science - Part C: Polymer Letters, 19(4), 205-210 (1981)
Preparation of PPV nanotubes and nanorods and carbonized products derived therefrom.
Kim K and Jin J.
Nano Letters, 1(11), 205-210 (1981)
Poly (p-phenylene vinylene) prepared by chemical vapor deposition: Influence of monomer selection and reaction conditions on film composition and luminescence properties.
Vaeth KM and Jensen KF.
Macromolecules, 31(20), 6789-6793 (1998)
Contact dermatitis caused by "chloromethyl heterocyclic intermediates".
H Ippen
Contact dermatitis, 16(1), 52-52 (1987-01-01)
Jing-Wei Xu et al.
Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 133, 148-155 (2015-06-22)
Electrospun nanofibers with antibacterial activity are greatly promising for medical treatment and water purification. Herein we report antibacterial nanofibers electrospun from a series of poly(dimethylamino ethyl methacrylate-co-alkyl methacrylates) (poly(DMAEMA-co-AMA)) and to distinguish the effects of free and cross-linked cations derived
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service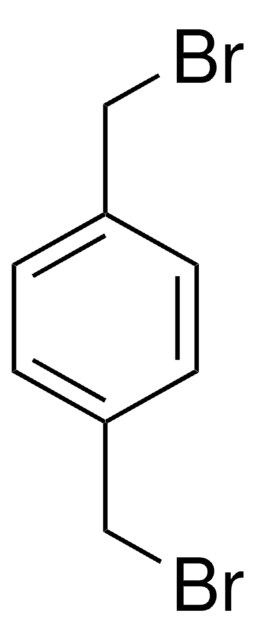








![[2.2]Paracyclophane 97%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/165/940/d2dda3d5-1fe9-4c87-9a85-009490e67661/640/d2dda3d5-1fe9-4c87-9a85-009490e67661.png)
