132632
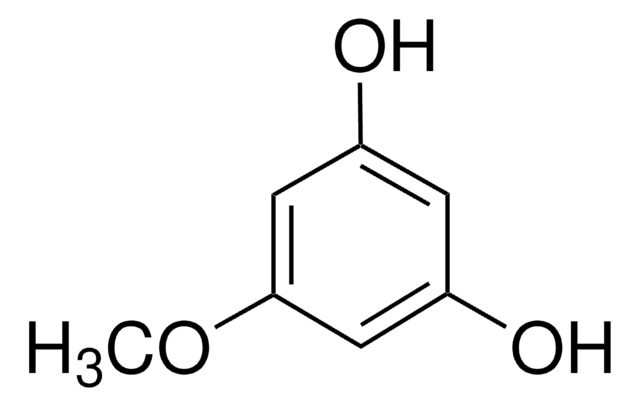
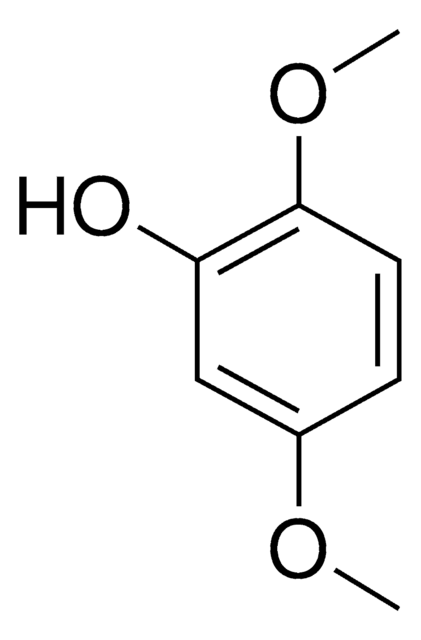
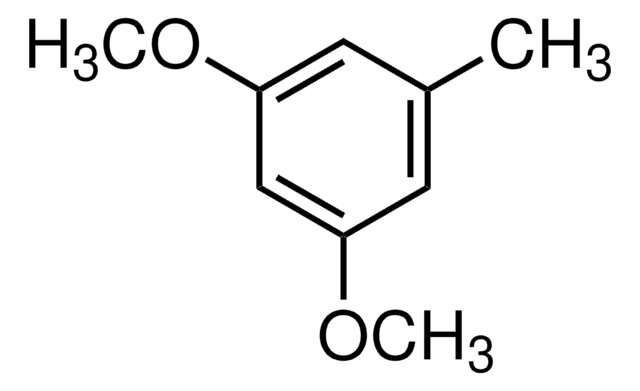
3,5-Dimethoxyphenol
99%
Synonym(s):
Phloroglucinol dimethyl ether
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
(CH3O)2C6H3OH
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
154.16
Beilstein:
1239156
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
solid
bp
172-175 °C/17 mmHg (lit.)
mp
40-43 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
COc1cc(O)cc(OC)c1
InChI
1S/C8H10O3/c1-10-7-3-6(9)4-8(5-7)11-2/h3-5,9H,1-2H3
InChI key
XQDNFAMOIPNVES-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
3,5-Dimethoxyphenol has been used in a study on iron porphyrin phenoxides. It was used to develop a new analytical method using LC-MS that enables the simultaneous identification and quantification of new alkaloids and the alkaloidal diterpenoids.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Iron porphyrin phenoxides: models for some hemoglobin mutants.
Ainscough E_W, et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 100(24), 7585-7591 (1978)
Laura Burga et al.
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 440(1), 54-64 (2005-07-19)
A cDNA was cloned from Ruta graveolens cells encoding a novel O-methyltransferase (OMT) with high similarity to orcinol or chavicol/eugenol OMTs, but containing a serine-rich N-terminus and a 13 amino acid insertion between motifs IV and V. Expression in Escherichia
R Froldi et al.
Journal of analytical toxicology, 34(1), 53-56 (2010-01-30)
Taxus baccata is a widely distributed yew often associated with cases of fatal intoxication, which is related to the high amounts of cardiotoxic alkaloids, taxine A and taxine B, contained in its leaves. In this paper, a case of Taxus
Claudia Panzeri et al.
Clinical toxicology (Philadelphia, Pa.), 48(5), 463-465 (2010-06-10)
Yew (Taxus baccata) is a conifer known to be toxic since ancient times. Taxine A and taxine B, the toxic alkaloids of Taxus, block cardiac sodium and calcium channels causing nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory distress, coma, seizures
Modern analytical procedures for the determination of taxus alkaloids in biological material.
F Musshoff et al.
International journal of legal medicine, 122(4), 357-358 (2008-05-07)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service