All Photos(2)
About This Item
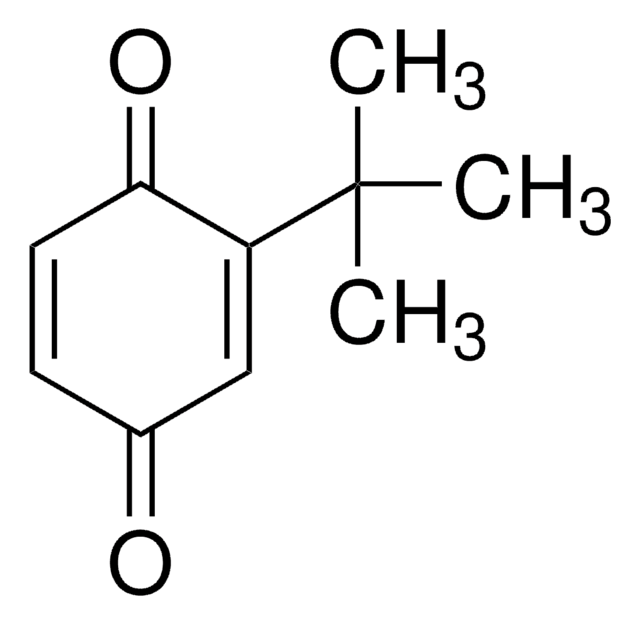
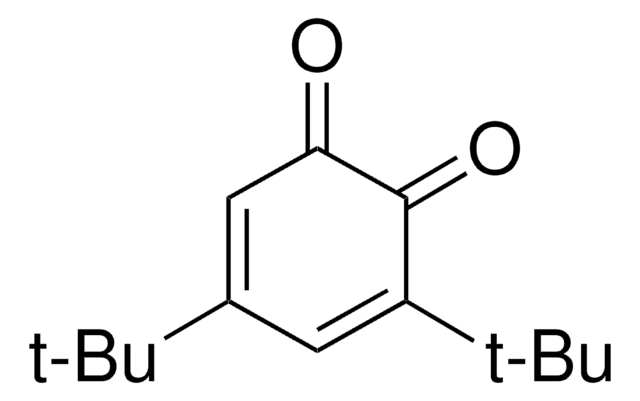
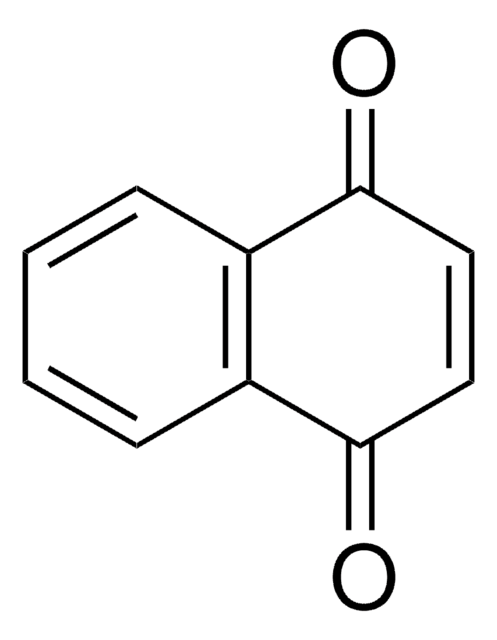
Linear Formula:
[(CH3)3C]2C6H2(=O)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
220.31
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Assay
99%
mp
152-154 °C (lit.)
functional group
ketone
SMILES string
CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=O)C(=CC1=O)C(C)(C)C
InChI
1S/C14H20O2/c1-13(2,3)9-7-12(16)10(8-11(9)15)14(4,5)6/h7-8H,1-6H3
InChI key
ZZYASVWWDLJXIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
2,5-Di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone (DTBBQ) is an 2,5-disubstituted quinone. It is an antibacterial compound. It has been isolated from marine Streptomyces sp. VITVSK1. Pressure dependance on the intramolecular and intermolecular migration rates of Na+ and K+ in a 2,5-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone ion pair have been evaluated by using a high-pressure EPR technique.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Pressure effects on cation migration in 2, 5-di-tert-butyl-1, 4-benzoquinone radical anion.
Kasahara M, et al.
International Journal of Chemical Kinetics, 33(7), 397-401 (2001)
H Westerblad et al.
The Journal of physiology, 474(2), 291-301 (1994-01-15)
1. Intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) and force were measured from isolated single mouse skeletal muscle fibres at rest and during tetani. The actions of 2,5-di(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone (TBQ), an inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ pump, were examined at a range
H Nakamura et al.
Journal of biochemistry, 112(6), 750-755 (1992-12-01)
We characterized the interaction of 2,5-di(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone (tBuBHQ) with the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+)-ATPase from rabbit fast-twitch skeletal and canine cardiac muscles by examining the effect of this agent on the ATPase reaction. tBuBHQ at less than 10 microM inhibited ATP
Y K Ju et al.
The Journal of physiology, 516 ( Pt 3), 793-804 (1999-04-14)
1. The mechanism by which sympathetic transmitters increase the firing rate of pacemaker cells was explored in isolated cells from the sinus venosus of the cane toad Bufo marinus. Intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) was measured with indo-1 and membrane potential
M T Clunes et al.
Cell calcium, 20(4), 339-346 (1996-10-01)
The human lung small cell adenocarcinoma cell line, A549, demonstrates a concentration-dependent rise in [Ca2+]i in response to extracellular nucleotides. The cells show Ca2+ mobilization on addition of various nucleotides, with an order of agonist potency: UTP > or =
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service