About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
10 mmHg ( 13.2 °C)
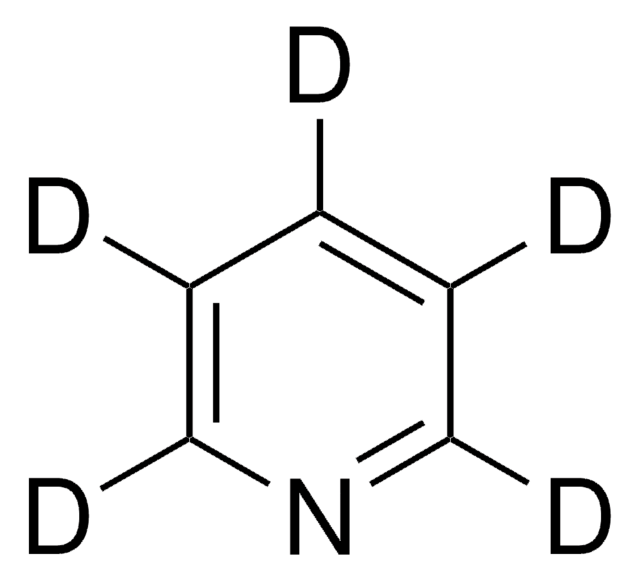
isotopic purity
98 atom % 15N
Assay
99% (CP)
bp
115 °C (lit.)
mp
−42 °C (lit.)
density
0.990 g/mL at 25 °C
mass shift
M+1
SMILES string
c1cc[15n]cc1
InChI
1S/C5H5N/c1-2-4-6-5-3-1/h1-5H/i6+1
InChI key
JUJWROOIHBZHMG-PTQBSOBMSA-N
Packaging
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
68.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
20 °C - closed cup
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service