764213
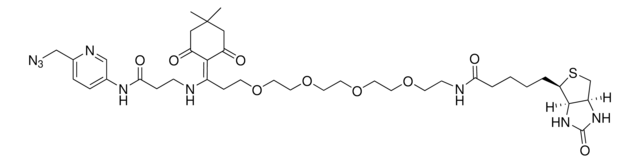
Biotin-PEG4-alkyne
for copper catalyzed click labeling
Synonym(s):
Polyethylene glycol, Acetylene-PEG4-biotin conjugate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
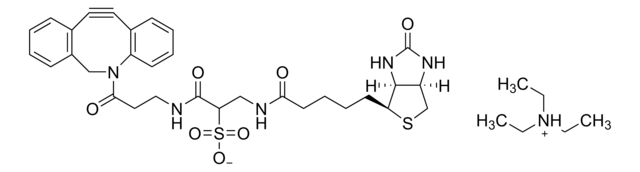
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C21H35N3O6S
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
457.58
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12161502
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
95%
form
solid
reaction suitability
reaction type: click chemistry
mp
55-64 °C
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
O=C(NCCOCCOCCOCCOCC#C)CCCC[C@@H](SC1)[C@@]2([H])[C@]1([H])NC(N2)=O
InChI
1S/C21H35N3O6S/c1-2-8-27-10-12-29-14-15-30-13-11-28-9-7-22-19(25)6-4-3-5-18-20-17(16-31-18)23-21(26)24-20/h1,17-18,20H,3-16H2,(H,22,25)(H2,23,24,26)/t17-,18-,20-/m1/s1
InChI key
SKMJWNZZFUDLKQ-QWFCFKBJSA-N
Related Categories
Application
Biotin-PEG4-alkyne may be used for the modification of 4-azidophenylalanine (AzPhe) silk fibroin via bioorthogonal azide–alkyne cycloaddition reaction for developing photopatternable protein material.
Biotinylation reagent for labeling azide containing molecules or biomolecules using copper-catalyzed 1,3 dipolar cycloaddition click chemistry. The alkyne group reacts with azides to form a stable triazole linkage, facilitating the introduction of biotin into your azide modified system of interest.
Automate your Biotin tagging with Synple Automated Synthesis Platform (SYNPLE-SC002)
Automate your Biotin tagging with Synple Automated Synthesis Platform (SYNPLE-SC002)
Other Notes
Chemoproteomic Profiling of Gut Microbiota-Associated Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity
Fluorescent Heterotelechelic Single-Chain Polymer Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Spectroscopy, and Cellular Imaging
Arginine-Selective Chemical Labeling Approach for Identification and Enrichment of Reactive Arginine Residues in Proteins
Selective Imaging of Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Microbiotas in the Mouse Gut
Metabolic Oligosaccharide Engineering with Alkyne Sialic Acids Confers Neuraminidase Resistance and Inhibits Influenza Reproduction
A Modular Probe Strategy for Drug Localization, Target Identification and Target Occupancy Measurement on Single Cell Level
Fluorescent Heterotelechelic Single-Chain Polymer Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Spectroscopy, and Cellular Imaging
Arginine-Selective Chemical Labeling Approach for Identification and Enrichment of Reactive Arginine Residues in Proteins
Selective Imaging of Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Microbiotas in the Mouse Gut
Metabolic Oligosaccharide Engineering with Alkyne Sialic Acids Confers Neuraminidase Resistance and Inhibits Influenza Reproduction
A Modular Probe Strategy for Drug Localization, Target Identification and Target Occupancy Measurement on Single Cell Level
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Azide-incorporated clickable silk fibroin materials with the ability to photopattern.
Teramoto H, et al.
ACS biomaterials science & engineering, 2(2), 251-258 (2016)
Vinita Lukose et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(39), 12446-12449 (2015-09-10)
The cell surfaces of bacteria are replete with diverse glycoconjugates that play pivotal roles in determining how bacteria interact with the environment and the hosts that they colonize. Studies to advance our understanding of these interactions rely on the availability
Torben Heise et al.
Bioconjugate chemistry, 28(7), 1811-1815 (2017-06-22)
Metabolic incorporation of azide- or alkyne-modified sialic acids into the cellular glycosylation pathway enables the study of sialoglycan expression, localization, and trafficking via bioorthogonal chemistry. Herein, we report that such modifications of the sialic acid sugar can have a profound
Anna Rutkowska et al.
ACS chemical biology, 11(9), 2541-2550 (2016-07-08)
Late stage failures of candidate drug molecules are frequently caused by off-target effects or inefficient target engagement in vivo. In order to address these fundamental challenges in drug discovery, we developed a modular probe strategy based on bioorthogonal chemistry that
Wei Wang et al.
Biochemistry, 56(30), 3889-3893 (2017-07-07)
The diverse gut microbial communities are crucial for host health. How the interactions between microbial communities and between host and microbes influence the host, however, is not well understood. To facilitate gut microbiota research, selective imaging of specific groups of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service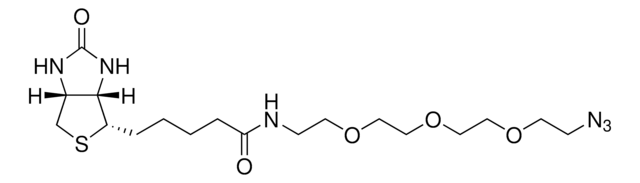
![Tris[(1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl]amine 97%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/179/695/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f/640/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f.png)