MAB1681
Anti-Vimentin Antibody, clone LN-6
culture supernatant, clone LN-6, Chemicon®
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
culture supernatant
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
LN-6, monoclonal
species reactivity
human, mouse
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
isotype
IgM
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... VIM(7431)
General description
Vimentin is a class III intermediate filament protein (homopolymers) found in various non-epithelial cells including mesenchymal cells and fibroblasts. In many cells of mesenchymal origin, it is one of the most prominent phosphoproteins, especially during cell division when enhanced phosphorylation of vimentin corresponds with the reorganization of vimentin filaments.
Specificity
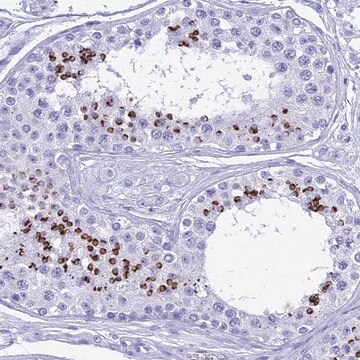
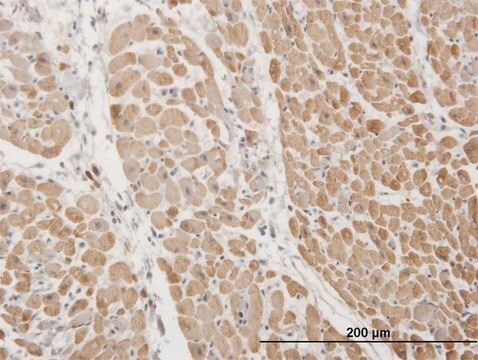
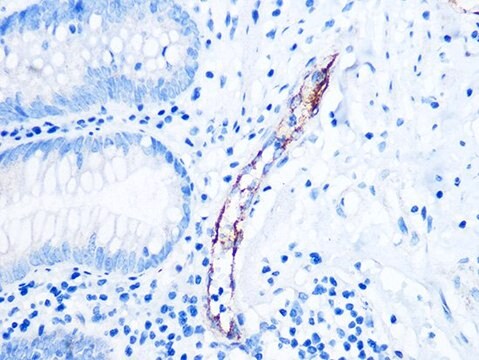
Reacts with human mesenchymal cells and derived sarcomas. Reacts with an epitope of the cytoskeletal protein vimentin but unlike other vimentin antibodies, does not react with human lymphoid cells or derived malignancies. Reactive with endothelium, muscle, fibroblasts, melanocytes, peripheral nerve, sertoli cells, kidney mesangial cells and tubules, osteoblasts and periosteum, non-hematopoietic tumors of mesenchymal origin (all sarcomas), meningiomas and melanomas.
Immunogen
Nuclei from adult human thymic biopsy specimens.
Application
Anti-Vimentin Antibody, clone LN-6 detects level of Vimentin & has been published & validated for use in IH(P).
Immunohistochemistry on B5 fixed, paraffin embedded tissue sections.
Target description
57-60 kDa
Physical form
Liquid tissue culture supernatant containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Analysis Note
Control
Hyperplastic lymph nodes.
Hyperplastic lymph nodes.
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
recommended
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Paola Valdivieso et al.
PloS one, 12(4), e0174864-e0174864 (2017-04-07)
Mechanical stress, including blood pressure related factors, up-regulate expression of the pro-angiogenic extracellular matrix protein tenascin-C in skeletal muscle. We hypothesized that increased capillarization of skeletal muscle with the repeated augmentation in perfusion during endurance training is associated with blood
Liqing Wang et al.
The Journal of comparative neurology, 524(11), 2322-2334 (2016-01-01)
Expression of Nogo protein was investigated in the optic pathway of embryonic mice by using isoform-specific antibodies Bianca and 11C7, which recognize Nogo-A/B and Nogo-A, respectively. Our previous reports from using antibody N18 have shown that Nogo is localized on
Francesca Cialdai et al.
Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 78(23), 7795-7812 (2021-10-30)
Astronauts on board the International Space Station (ISS) are exposed to the damaging effects of microgravity and cosmic radiation. One of the most critical and sensitive districts of an organism is the eye, particularly the retina, and > 50% of astronauts develop
Maria Elena Melica et al.
Stem cell research & therapy, 15(1), 20-20 (2024-01-18)
The glomerulus is a highly complex system, composed of different interdependent cell types that are subjected to various mechanical stimuli. These stimuli regulate multiple cellular functions, and changes in these functions may contribute to tissue damage and disease progression. To
David P J Hunt et al.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio), 26(1), 163-172 (2007-09-29)
Skin-derived precursor cells (SKPs) are multipotent neural crest-related stem cells that grow as self-renewing spheres and are capable of generating neurons and myelinating glial cells. SKPs are of clinical interest because they are accessible and potentially autologous. However, although spheres
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service