MAB377B
Anti-NeuN Antibody, clone A60, biotin conjugated
clone A60, Chemicon®, from mouse
Synonym(s):
Neuron-Specific Nuclear Protein
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
biotin conjugate
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
A60, monoclonal
species reactivity
rat, mouse
species reactivity (predicted by homology)
ferret, salamander, human, chicken
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG1
shipped in
wet ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... RBFOX3(146713)
mouse ... Rbfox3(52897)
rat ... Rbfox3(287847)
General description
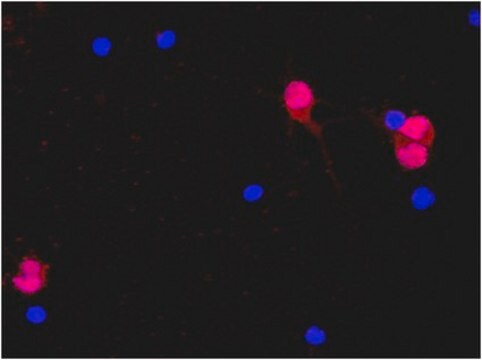
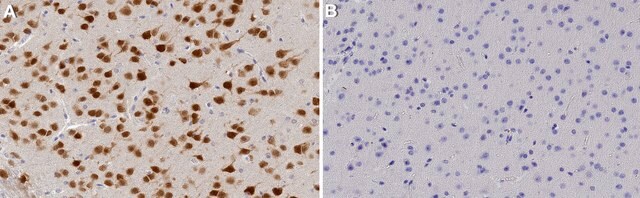
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
1:10-1:500 dilution of a previous lot was used. Neurons in culture should be permeablized with 0.1% triton X-100. All primary antibody dilutions should be performed with simple solutions containing only buffer and primary antibody without excess protein blocks or detergents.
For dual labeling studies using mouse monoclonals, antibody incubations should be sequential with MAB377B last. First mouse monoclonal antibody should be first detected with anti-mouse secondary prior to incubating with MAB377B. Excess anti-mouse IgG may be blocked by incubating with 1% mouse serum prior to MAB377B incubation. Detection of biotinylated NeuN monoclonal is via streptavidin. In some cases in may be necessary to pretreat the tissue with avidin to block excess biotin prior to immunohistochemisty (Wood and Warnke, 1981).
Immunohistochemistry:
1:200-1:2,000. The antibody works best on polyester wax embedded tissue but also works on paraffin embedded tissue at a lower working dilution. The antibody works well with formaldehyde-based fixatives. Citric acid and microwave pretreatment has been used successfully (Sarnat, 1998).
Western Blotting Analysis:
A previous lot of this antibody was used on western blot. Recognizes 2-3 bands in the 46-48 kDa range and possibly another band at approximately 66 kDa.
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Neuroscience
Neuronal & Glial Markers
Quality
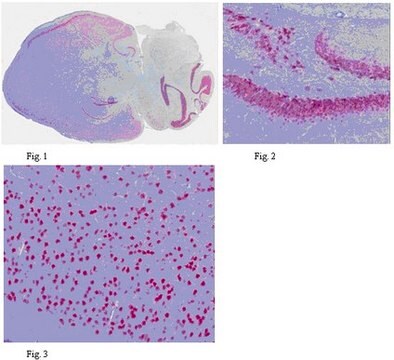
Immunohistochemistry(paraffin) Analysis:
NeuN (cat. # MAB377B) staining pattern/morphology in rat cerebellum. Tissue pretreated with Citrate, pH 6.0. This lot of antibody was diluted to 1:100, using IHC-Select Detection with HRP-DAB. Immunoreactivity is seen as nuclear staining in the neurons in the granular layer. Note that there is no signal detected in the nucleus of Purkinje cells.
Optimal Staining With Citrate Buffer, pH 6.0, Epitope Retrieval: Rat Cerebellum
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Analysis Note
Brain tissue, most neuronal cell types throughout the adult nervous system
Other Notes
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service