A3913
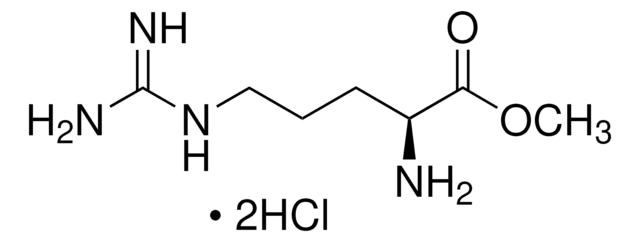
L-Argininamide dihydrochloride
≥98%, suitable for ligand binding assays
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C6H15N5O · 2HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
246.14
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
Product Name
L-Argininamide dihydrochloride,
Assay
≥98%
Quality Level
form
powder
technique(s)
ligand binding assay: suitable
color
white to off-white
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.N[C@@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(N)=O
InChI
1S/C6H15N5O.ClH/c7-4(5(8)12)2-1-3-11-6(9)10;/h4H,1-3,7H2,(H2,8,12)(H4,9,10,11);1H/t4-;/m0./s1
InChI key
BPQLYFCEVVKLLX-WCCKRBBISA-N
Application
L-Argininamide dihydrochloride has been used as an additive to compare its effect over L-arg in egg lysozyme refolding studies. It has also been used as a component of substrate stock solution for enzymatic kyotorphin synthesis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-Argininamide (L-Arm) is a hydrophilic amino acid derivative that is used as a model compound in physicochemical characteristic studies of ligand binding DNA aptamers and their potential development as fluorescent aptasensors.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - STOT SE 1
Target Organs
Eyes
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Max Keller et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 19(9), 2859-2878 (2011-04-16)
Fluorescently labelled NPY Y(1) receptor (Y(1)R) ligands were synthesized by connecting pyrylium and cyanine dyes with the argininamide-type Y(1)R antagonist core structure by linkers, covering a wide variety in length and chemical nature, attached to the guanidine group. The most
Label-free aptamer-based sensors for L-argininamide by using nucleic acid minor groove binding dyes.
Zece Zhu et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 47(11), 3192-3194 (2011-01-29)
The nucleic acid minor groove binding dyes, DAPI and Hoechst 33258, were for the first time used in label-free aptamer-based sensors for L-argininamide. The synergy binding effect results in the enhancement of fluorescence of dyes. The method for detection of
G Reid Bishop et al.
Biophysical chemistry, 126(1-3), 165-175 (2006-08-18)
The thermal stability and ligand binding properties of the L-argininamide-binding DNA aptamer (5'-GATCGAAACGTAGCGCCTTCGATC-3') were studied by spectroscopic and calorimetric methods. Differential calorimetric studies showed that the uncomplexed aptamer melted in a two-state reaction with a melting temperature T(m)=50.2+/-0.2 degrees C
Zhiai Xu et al.
Biosensors & bioelectronics, 26(12), 4733-4738 (2011-07-02)
Aptamers are nucleic acids that can selectively bind to a variety of targets. Aptamers usually undergo conformational transitions from a flexible or disordered structure into a rigid or ordered structure upon target-binding. This study describes a detection method for l-argininamide
Tao Li et al.
Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 13(23), 6718-6723 (2007-05-17)
We report a novel label-free method for the investigation of the adaptive recognition of small molecules by nucleic acid aptamers using capillary electrophoresis analysis. Cocaine and argininamide were chosen as model molecules, and the two corresponding DNA aptamers were used.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service