A5062
Anti-Guinea Pig IgG (whole molecule)−Alkaline Phosphatase antibody produced in goat
affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
goat
Quality Level
conjugate
alkaline phosphatase conjugate
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
secondary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
technique(s)
direct ELISA: 1:30,000
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:50
western blot: 1:30,000
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
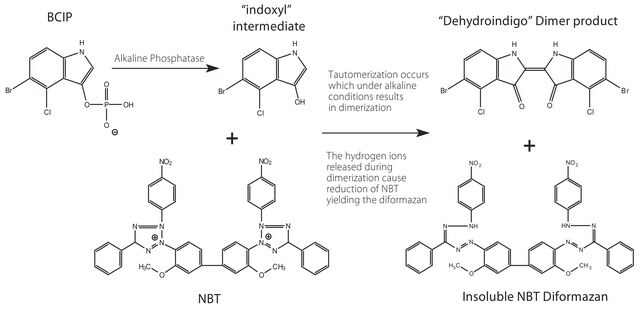
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a glycoprotein antibody that regulates immune responses such as phagocytosis and is also involved in the development of autoimmune diseases . In guinea pig IgG is subdivided into-IgG1 and IgG2. IgG2 can bind to Fc receptor of macrophages and monocytes. Anti-guinea pig IgG (whole molecule) −alkaline phosphatase antibody can be used in immunohistology (diluted 1:50). Goat anti-guinea pig IgG (whole molecule) −alkaline phosphatase antibody reacts specifically with guinea pig IgG.
Immunogen
Purified guinea pig IgG.
Application
Anti-guinea pig IgG (whole molecule) −alkaline phosphatase antibody can be used in direct ELISA (diluted 1:30,000) and dot blot.
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Western blot analysis of SF9 cells was performed using alkaline phosphatase conjugated goat anti-guinea pig IgGat 1:10000 as the secondary.
Physical form
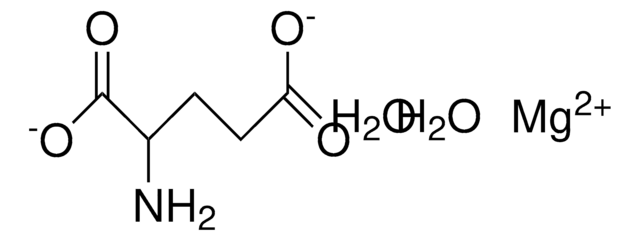
Solution in 0.05 M Tris, pH 8.0, containing 1 mM MgCl2, 10 mM glycine, 1% bovine serum albumin, 50% glycerol and 15 mM sodium azide
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Anahita Daryabeigi et al.
Genetics, 203(2), 733-748 (2016-04-22)
SUN (Sad1 and UNC-84) and KASH (Klarsicht, ANC-1, and Syne homology) proteins are constituents of the inner and outer nuclear membranes. They interact in the perinuclear space via C-terminal SUN-KASH domains to form the linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC)
M D Alexander et al.
Immunology, 35(1), 115-123 (1978-07-01)
Guinea-pig IgG2 and IgT1 bind to contiguous Fc receptors on homologous peritoneal macrophages. Equilibrium association constants determined for the binding of human IgG subclasses to homologous peripheral blood monocytes show that the order of binding is IgG1 greater than IgG3
Jens Modrof et al.
Journal of virology, 79(15), 10023-10031 (2005-07-15)
In bluetongue virus (BTV)-infected cells, large cytoplasmic aggregates are formed, termed viral inclusion bodies (VIBs), which are believed to be the sites of viral replication and morphogenesis. The BTV nonstructural protein NS2 is the major component of VIBs. NS2 undergoes
Philippe P Pagni et al.
Diabetes, 63(6), 2015-2025 (2014-02-13)
Type 1 diabetes is thought to be an autoimmune condition in which self-reactive T cells attack insulin-secreting pancreatic β-cells. As a proinflammatory cytokine produced by β-cells or macrophages, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) represents a potential therapeutic target in diabetes. We reasoned IL-1β
Mazhar Hussain et al.
iScience, 26(1), 105836-105836 (2023-01-14)
The endosymbiotic bacterium Wolbachia pipientis blocks replication of several arboviruses in transinfected Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. However, the mechanism of virus blocking remains poorly understood. Here, we characterized an RNase HI gene from Wolbachia, which is rapidly induced in response to
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service