L2261
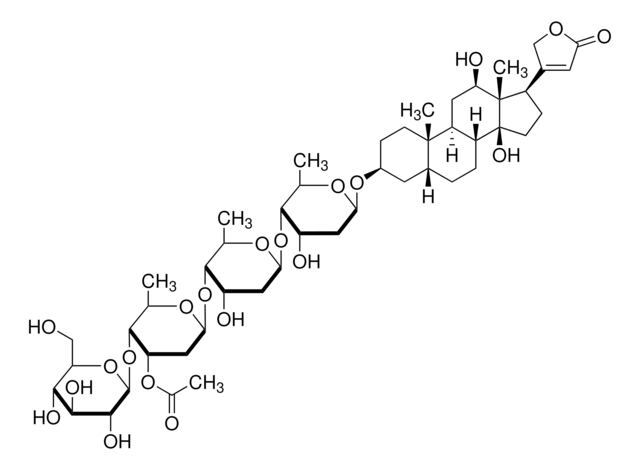
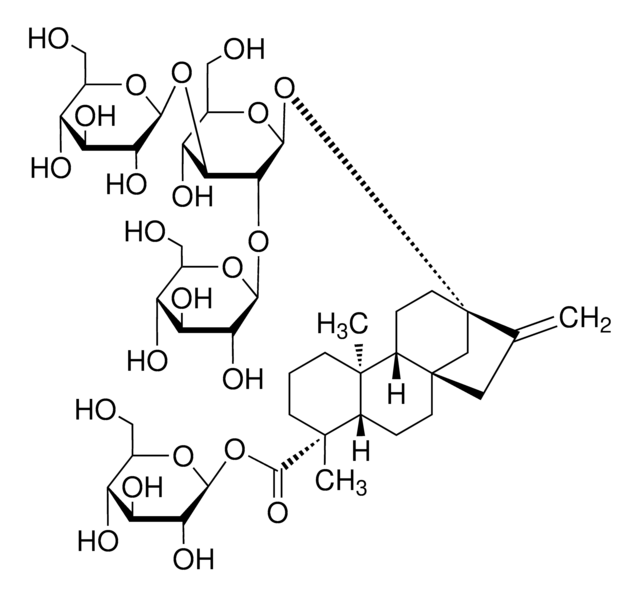
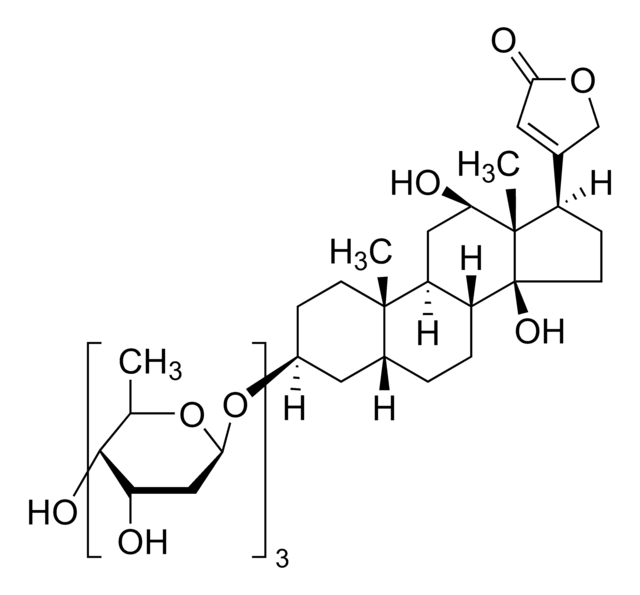
Lanatoside C
≥97% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
Digilanide C, Digilanogen C, Isolanide, Lanatigen C
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥97% (TLC)
form
powder
color
white
storage temp.
−20°C
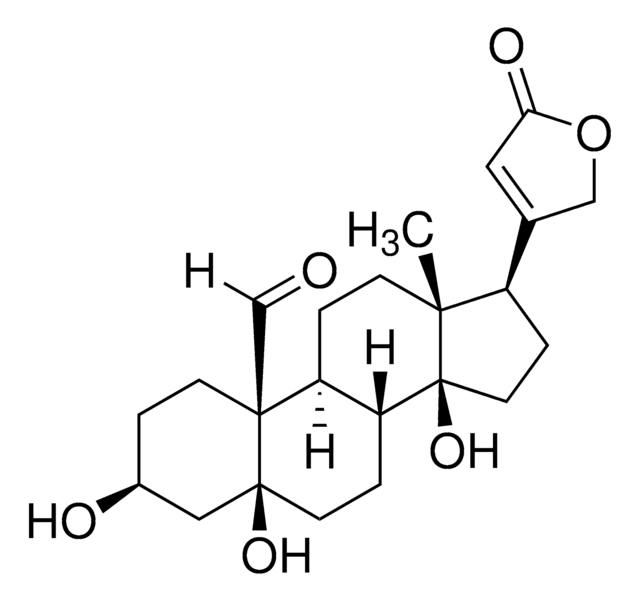
SMILES string
C[C@H]1O[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@H](O[C@H]3C[C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@H](O[C@@H]4O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]4O)[C@@H](C)O3)[C@@H](C)O2)O[C@H]5CC[C@@]6(C)[C@H](CC[C@@H]7[C@@H]6C[C@@H](O)[C@]8(C)[C@H](CC[C@]78O)C9=CC(=O)OC9)C5
InChI
1S/C49H76O20/c1-21-43(67-38-17-32(53)44(22(2)62-38)68-39-18-33(64-24(4)51)45(23(3)63-39)69-46-42(58)41(57)40(56)34(19-50)66-46)31(52)16-37(61-21)65-27-9-11-47(5)26(14-27)7-8-29-30(47)15-35(54)48(6)28(10-12-49(29,48)59)25-13-36(55)60-20-25/h13,21-23,26-35,37-46,50,52-54,56-59H,7-12,14-20H2,1-6H3/t21-,22-,23-,26-,27+,28-,29-,30+,31+,32+,33+,34-,35-,37+,38+,39+,40-,41+,42-,43-,44-,45-,46+,47+,48+,49+/m1/s1
InChI key
JAYAGJDXJIDEKI-PTGWOZRBSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Cardiac glycoside sensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma: Research demonstrated that Lanatoside C enhances the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through mechanisms involving reactive oxygen species generation, p38MAPK activation, and modulation of mitochondrial transition and autophagy (Rasheduzzaman et al., 2019).
- Elimination of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells: Lanatoside C has been shown to selectively eliminate undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells, indicating its potential use in ensuring the safety of stem cell-derived therapies (Lin et al., 2017).
Other Notes
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - STOT RE 2
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service