378348
Silicone oil
viscosity 20 cSt (25 °C)
Synonym(s):
PDMS, Polydimethylsiloxane
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
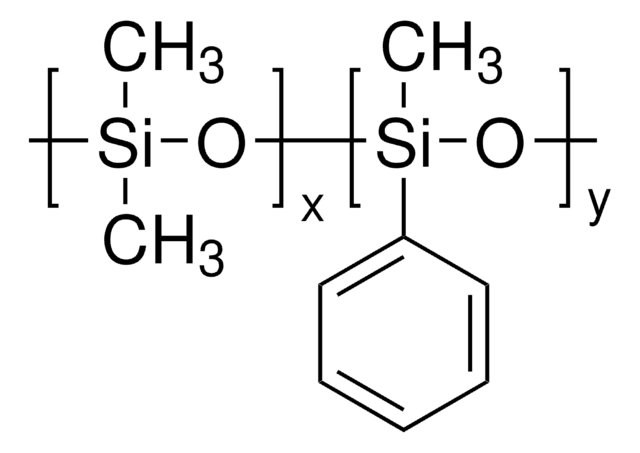
[-Si(CH3)2O-]n
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
vapor density
>1 (vs air)
vapor pressure
<5 mmHg ( 25 °C)
5 mmHg ( 20 °C)
form
viscous liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.403 (lit.)
viscosity
20 cSt(25 °C)
bp
>140 °C/0.002 mmHg (lit.)
density
0.95 g/mL at 25 °C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Silicone oil is a liquid based siloxane that is part of the methyl silicone fluid system. It has a viscosity of 20 cSt with a refractive index of ~ 1.4 and a dielectric strength of ~ 14 kV/mm. It′s surface tension tends to increase with an increase in the viscosity.
Application
Silicone oil can be used for a variety of usages such as lubricants, antiflatulent agents, dielectric coolants, and cosmetic additives.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
214.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
101.1 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Antifoaming agents
Owen MJ
Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, 104(2), 527-535 (2001)
Silicones
Moretto H, et al.
Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (2000)
Mechanism of Stabilization of Silicone Oil- Water Emulsions Using Hybrid Siloxane Polymers
Mehta SC and Somasundaran P
Langmuir, 24(9), 4558-4563 (2008)
Gary R Skuse et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1001, 99-114 (2013-03-16)
Our ability to manipulate stem cells in order to induce differentiation along a desired developmental pathway has improved immeasurably in recent years. That is in part because we have a better understanding of the intracellular and extracellular signals that regulate
Amir Sanati Nezhad et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(20), 8093-8098 (2013-05-01)
Tip-growing cells have the unique property of invading living tissues and abiotic growth matrices. To do so, they exert significant penetrative forces. In plant and fungal cells, these forces are generated by the hydrostatic turgor pressure. Using the TipChip, a
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service