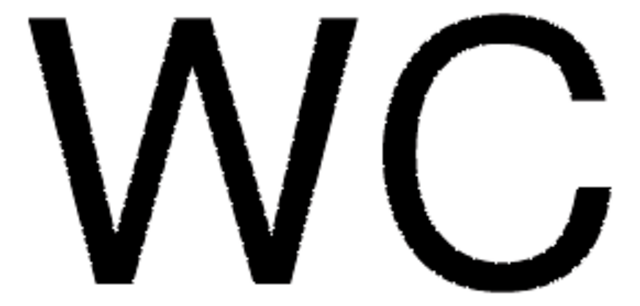594849
Titanium(IV) carbide
powder, <4 μm, ≥99% (Ti)
Synonym(s):
TiC-HP, Titanium monocarbide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
TiC
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
59.88
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352300
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Assay
≥99% (Ti)
form
powder
particle size
<4 μm
bp
4820 °C (lit.)
mp
3140 °C (lit.)
density
4.930 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
[C-]#[Ti+]
InChI
1S/C.Ti/q-1;+1
InChI key
YXIVWSJCLXKLJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Hiroshi Moriwaki et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 185(2-3), 725-731 (2010-10-26)
The aim of this study is to investigate the utilization of the powder of porous titanium carbide (TiC) ceramics as a novel adsorbent or a material for solid-phase extraction (SPE). The adsorption and elution of inorganic and organic pollutants, Pb(II)
Yong Luo et al.
Journal of biomechanics, 42(16), 2708-2711 (2009-10-20)
Titanium cermet was successfully synthesized and formed a thin gradient titanium carbide coating on the surface of Ti6Al4V alloy by using a novel sequential carburization under high temperature, while the titanium cermet femoral head was produced. The titanium cermet phase
Jochen Rohrer et al.
Journal of physics. Condensed matter : an Institute of Physics journal, 22(47), 472001-472001 (2011-03-10)
We investigate the chemical composition and adhesion of chemical vapour deposited thin-film alumina on TiC using and extending a recently proposed nonequilibrium method of ab initio thermodynamics of deposition growth (AIT-DG) (Rohrer and Hyldgaard 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 045415).
Woo Sik Kim et al.
Nanotechnology, 21(5), 055608-055608 (2010-01-07)
Single-phase layered titanium carbide (TiC) was successfully synthesized by reacting carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) under a high direct current (DC) pulse. Single-phase TiC layer fabrication is confirmed as the transformation of multi-layered graphene from MWCNTs. Therefore its
Marina Brama et al.
Biomaterials, 28(4), 595-608 (2006-10-20)
Titanium has limitations in its clinical performance in dental and orthopaedic applications. This study describes a coating process using pulsed laser deposition (PLD) technology to produce surfaces of titanium carbide (TiC) on titanium substrates and evaluates the biological response both
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service