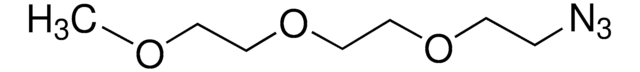
689440
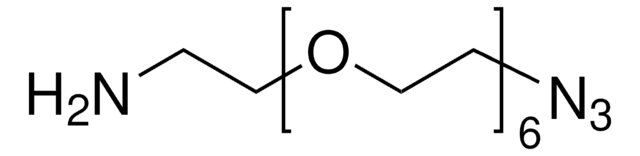
O-(2-Azidoethyl)heptaethylene glycol
≥95% (oligomer purity)
Synonym(s):
Azido-PEG (n=7)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
≥95% (oligomer purity)
form
powder
mol wt
average Mn 400
reaction suitability
reaction type: click chemistry
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
Ω-end
hydroxyl
α-end
azide
functional group
azide
hydroxyl
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCN=[N+]=[N-]
InChI
1S/C16H33N3O8/c17-19-18-1-3-21-5-7-23-9-11-25-13-15-27-16-14-26-12-10-24-8-6-22-4-2-20/h20H,1-16H2
InChI key
BUMODEBRFGPXRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
Some of the reported applications include:
- Synthesis of strain-stiffening hydrogels through self-assembly of oligomers fibres derived from Azido-PEG (n=7).
- Synthesis of biodegradable tetra-PEG hydrogels for drug delivery system.
- Synthesis of heterobifunctional oligo(ethylene glycol) linkers for bioconjugation and targeted drug delivery.
- Preparation of synthetic amphiphiles for programmed pH-dependent dispersions of carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
- Selective glycoprotein detection through allosteric click-imprinting by using a self-assembled monolayer developed from the above oligomer.
- Preparation of bioactivated quantum dot micelles containing fluorescent nanocrystals.
Packaging
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Designing biomaterial scaffolds mimicking complex living tissue structures is crucial for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine advancements.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service![2-[2-(2-Azidoethoxy)ethoxy]ethanol solution ~0.5 M in tert-butyl methyl ether](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/374/007/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a/640/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a.png)


![2-[2-(2-Chloroethoxy)ethoxy]ethanol 96%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/902/295/ff6d7bb1-a7e0-4582-86e1-819084626e67/640/ff6d7bb1-a7e0-4582-86e1-819084626e67.png)