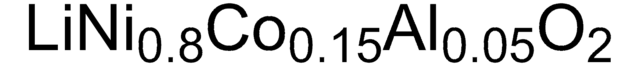759546
Lithium iron(II) phosphate
powder, <5 μm particle size (BET), >97% (XRF)
Synonym(s):
Ferrous lithium phosphate, Iron lithium phosphate, LFP, Triphylite
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
battery grade
Assay
>97% (XRF)
form
powder
mol wt
Mw 157.76 g/mol
composition
LiFePO4
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
particle size
<5 μm (BET)
mp
>300 °C (lit.)
density
3.6 g/cm3 (lit.)
application(s)
battery manufacturing
greener alternative category
InChI
1S/Fe.Li.H3O4P/c;;1-5(2,3)4/h;;(H3,1,2,3,4)/q+2;+1;/p-3
InChI key
GELKBWJHTRAYNV-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Features and Benefits
✔ Achieves 1000s of cycles
✔ Safer than cobalt or manganese-based cathode materials
✔ Reliable performance
Legal Information
related product
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Professor Qiao's review explores stable microstructures for lithium metal fluoride batteries, advancing energy storage technologies.
Solid oxide fuel cells and electrolyzers show potential for chemical-to-electrical energy conversion, despite early development stages.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service