MRN10
GenElute™ mRNA Miniprep Kit
sufficient for 10 purifications
Synonym(s):
GenElute™ mRNA Kit, Gen Elute
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41105501
NACRES:
NA.52
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 10 purifications
technique(s)
RNA purification: suitable
storage temp.
15-25°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
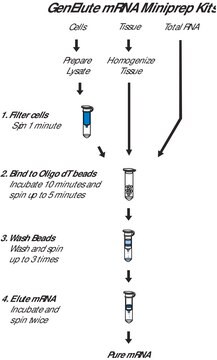
Procedures such as cDNA synthesis, expression profiling and others require separation of mRNA from the vastly more abundant rRNA and tRNA. The GenElute mRNA kits provide convenient procedures for isolating polyadenylated mRNA from previously prepared total RNA or directly from mammalian cells and tissues. For direct mRNA preparation, cells or tissues are disrupted with SDS/proteinase K digestion to release RNA and eliminate RNases. Both kit types use oligo dT30 covalently linked to 1 μm polystyrene beads to capture polyadenylated mRNA by hybridization. The polystyrene beads remain suspended during hybridization, eliminating the need for mixing or rocking, as is common for cellulose or magnetic particles. Polystyrene was also chosen because oligo(dT) polystyrene beads yield cleaner mRNA with fewer stringent washing steps than does the more commonly used oligo(dT) cellulose (2 or 3 wash steps versus 10 or more). With the GenElute kits, mRNA-bead complexes are washed on a microcentrifuge spin filter, and eluted into 10 mM Tris-HCL, pH 7.5. mRNA prepared with either kit is suitable for a variety of downstream applications such as Northern blotting, expression array or chip hybridizations and cDNA synthesis and library construction.
Application
The purified mRNA is ready for Northern analysis, reverse transcription and PCR, labeling for arrays, and other common applications.
Features and Benefits
- Quick and convenient reagent for use in the simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and protein
- Performs well with large or small amounts of tissue or cells and many samples can be simultaneously extracted
- One of the most effective methods for isolating total RNA. Purifications can be completed in only one hour starting with fresh tissue or cells
Other Notes
For additional information, please see www.sigma-aldrich.com/mrna.
Legal Information
GenElute is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Gang Luo et al.
Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 11(11) (2022-06-11)
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent internal mRNA modification in eukaryotes. The M6A modification plays an important role in transcription and cell function. The mechanism by which m6A modification regulates meat quality remains elusive. In this study, gene knockout and
Jianzi Lan et al.
Cellular & molecular biology letters, 27(1), 51-51 (2022-06-28)
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is prevalent in patients with diabetes. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation has been found to cause modification of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich repeat, and pyrin domain-containing (NLRP) 3, which is involved in cell pyroptosis and inflammation. WTAP is a
Kaiping Deng et al.
Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids, 26, 34-48 (2021-09-14)
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays a critical role in mammalian development. However, the role of m6A in the skeletal muscle development remains largely unknown. Here, we report a global m6A modification pattern of goat skeletal muscle at two key development stages
Weihong Xu et al.
Cell death & disease, 13(8), 715-715 (2022-08-18)
Gastric cancer (GC) is a malignancy with poor prognosis. NDUFA4 is reported to correlate with the progression of GC. However, its underlying mechanism in GC is unknown. Our study was to reveal the pathogenic mechanism of NDUFA4 in GC. NDUFA4
Caitlin M A Simopoulos et al.
G3 (Bethesda, Md.), 9(8), 2511-2520 (2019-06-27)
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent a diverse class of regulatory loci with roles in development and stress responses throughout all kingdoms of life. LncRNAs, however, remain under-studied in plants compared to animal systems. To address this deficiency, we applied a
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service