10836
Silicone oil AR 20
viscosity ~20 mPa.s, neat(25 °C)
Synonym(s):
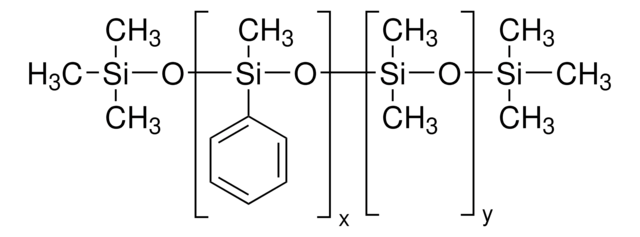
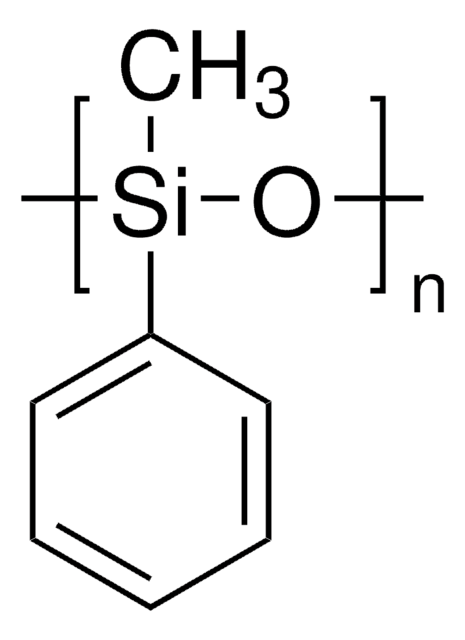
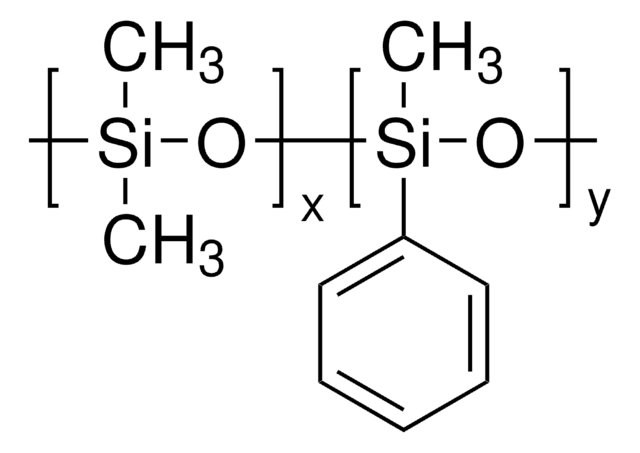
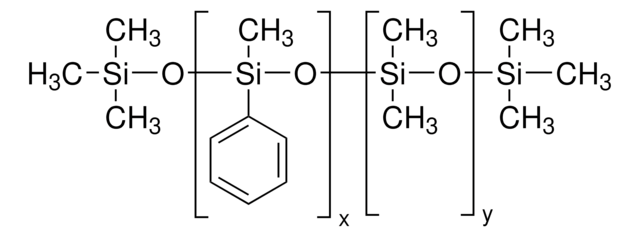
Polyphenyl-methylsiloxane
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
refractive index
n20/D 1.441-1.445
Quality Level
viscosity
~20 mPa.s, neat(25 °C)
density
1.000-1.020 g/mL at 20 °C
General description
Silicone oil AR 20 is a polydimethylsiloxane with phenyl groups that is commonly used as a heat transfer or pressure transfer fluid.
Application
Silicone oil AR 20 has been used:
- As a Segmenting fluid in polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- In hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction (LPME) procedure for extraction of hydrophobic drugs from human breast milk.
- As a fluid to demonstrate pores in droplet interface bilayers (DIBs).
Features and Benefits
Especially good thermostability (-50°C to +230°C)
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
338.0 °F - Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
170 °C - Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Liquid-phase microextraction of drugs from human breast milk
Bj?rhovde, A, et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 491(2), 155-161 (2003)
Formation of droplet interface bilayers in a Teflon tube
Walsh E, et al.
Scientific reports, 6(2), 34355-34355 (2016)
E J Walsh et al.
Biomedical microdevices, 7(4), 269-272 (2006-01-13)
This paper evaluates the compatibility of segmenting fluids for two phase flow applications in biomedical microdevices. The evaluated fluids are chosen due to the variations in fluid properties and cost, while also reflecting their use in the recent literature. These
H Kriegs et al.
The Journal of chemical physics, 124(10), 104901-104901 (2006-03-18)
In some polymers, in addition to the usual structural alpha relaxation, a slower alpha' relaxation is observed with a non-Arrhenius temperature dependence. In order to understand better the molecular origin of this alpha' relaxation in poly(methylphenylsiloxane) (PMPS) we have studied
C Eckardt et al.
Ophthalmologica. Journal international d'ophtalmologie. International journal of ophthalmology. Zeitschrift fur Augenheilkunde, 201(3), 133-139 (1990-01-01)
Different methylphenylsilicone (MPS) and fluorosilicone (FS) oils having a higher specific gravity than water were investigated as vitreous replacements. Their intraocular tolerance in vitrectomized aphakic rabbit eyes was evaluated for periods of up to 4 months and compared to that
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service