All Photos(1)
About This Item
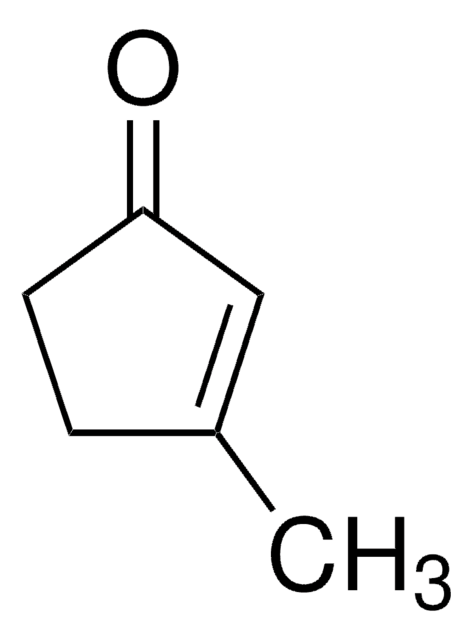
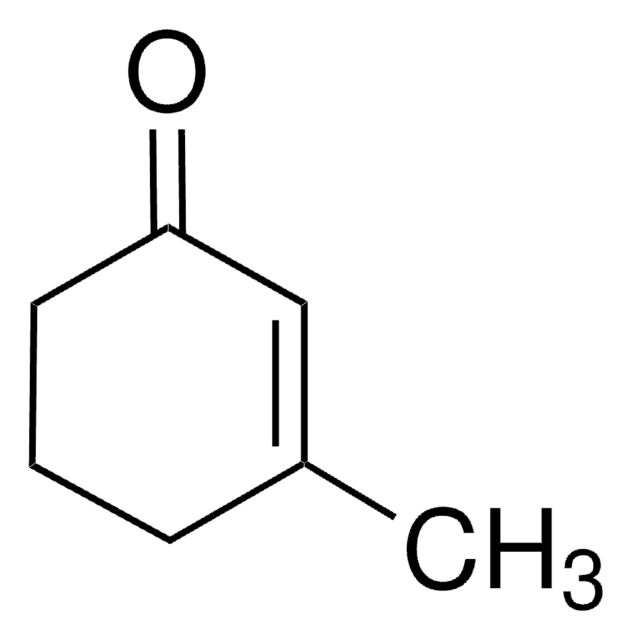
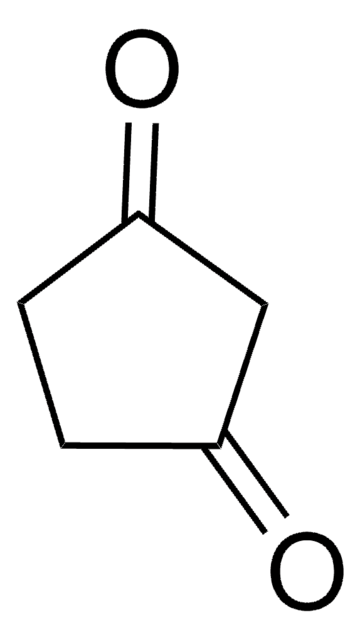
Linear Formula:
CH3C5H7(=O)
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
98.14
Beilstein:
1305074
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.434 (lit.)
bp
145 °C (lit.)
density
0.913 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
functional group
ketone
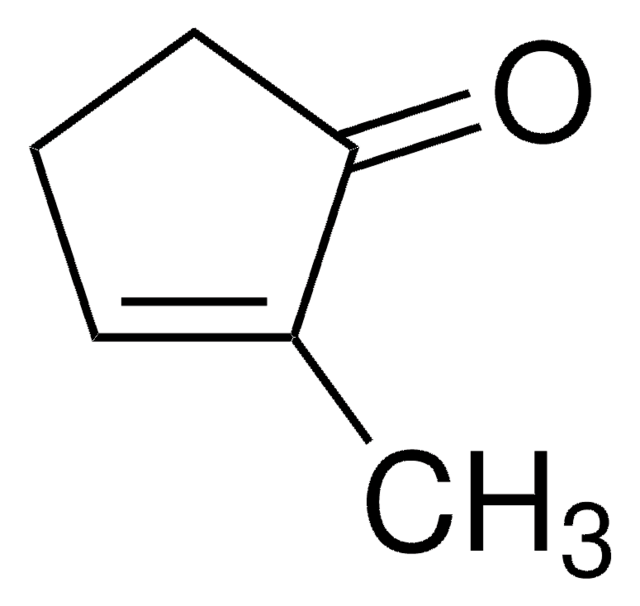
SMILES string
CC1CCC(=O)C1
InChI
1S/C6H10O/c1-5-2-3-6(7)4-5/h5H,2-4H2,1H3
InChI key
AOKRXIIIYJGNNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
3-Methylcyclopentanone is a monocyclic ketone and its optical rotatory dispersion has been studied under isolated and solvated conditions to explore the role of ring size/morphology. The vibrationally resolved electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra of (R)-(+)-3-methylcyclopentanone in gas phase was evaluated by density functional theory.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Liq. 3
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
93.2 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
34 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Priyanka Lahiri et al.
The journal of physical chemistry. A, 117(47), 12382-12400 (2013-11-15)
The optical rotatory dispersion of two monocyclic ketones, (R)-3-methylcyclopentanone [R-3MCP] and (R)-3-methylcyclohexanone [R-3MCH], has been investigated under isolated and solvated conditions to explore the role of ring size/morphology and to elucidate the impact of environmental perturbations. Vapor-phase measurements of specific
Na Lin et al.
The journal of physical chemistry. A, 112(48), 12401-12411 (2008-11-13)
The vibrationally resolved electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra of the two dominant conformers of (R)-(+)-3-methylcyclopentanone in gas phase are computed by density functional response theory, with a full account of Franck-Condon and Herzberg-Teller vibrational contributions at the harmonic level. Proper
Kajetan Koperwas et al.
Scientific reports, 6, 36934-36934 (2016-11-25)
When we cool down a liquid below the melting temperature, it can either crystallize or become supercooled, and then form a disordered solid called glass. Understanding what makes a liquid to crystallize readily in one case and form a stable
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service