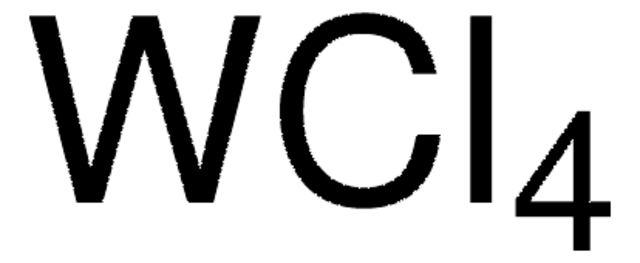241911
Tungsten(VI) chloride
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Tungsten hexachloride
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
43 mmHg ( 215 °C)
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.9% trace metals basis
form
powder
reaction suitability
reagent type: catalyst
core: tungsten
impurities
≤1000.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
bp
347 °C (lit.)
mp
275 °C (lit.)
density
3.52 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Cl[W](Cl)(Cl)(Cl)(Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/6ClH.W/h6*1H;/q;;;;;;+6/p-6
InChI key
KPGXUAIFQMJJFB-UHFFFAOYSA-H
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- As a starting material to synthesize tungsten nanoparticles and Mo-doped urchin-like W18O49 Nanostructure using the hydrothermal method. The Mo-W18O49 electrocatalyst exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activity toward Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER). By doping Mo species into defect-rich W18O49 ultrathin nanowires, it has also been demonstrated to be an excellent candidate for photocatalytic N2 fixation to ammonia.
- To synthesize crystalline mesoporous WO3 with 11 nm pore size utilizing a high-molecular-weight amphiphilic block copolymer as the structure-directing agent. The materials performed admirably in terms of H2S gas sensing.
- To fabricate Tungsten disulfide and WS2/reduced graphene oxide (WS2/rGO) nanosheets by hydrothermal synthesis. The WS2/rGO nanosheets showed exceptional electrocatalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- To produce the WS2-nanoflowers@rGO and nitrogen-doped carbon spheres@WS2 composite as an anode material for enhanced electrode performance in lithium-ion batteries.
- As a dopant to fabricate TiO2 compact layers for perovskite solar cells with enhanced performance.
- As a catalyst to prepare self-healing epoxy composites with microcapsules.
- As a catalyst for transamidation of tertiary alkyl amides.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service