282014
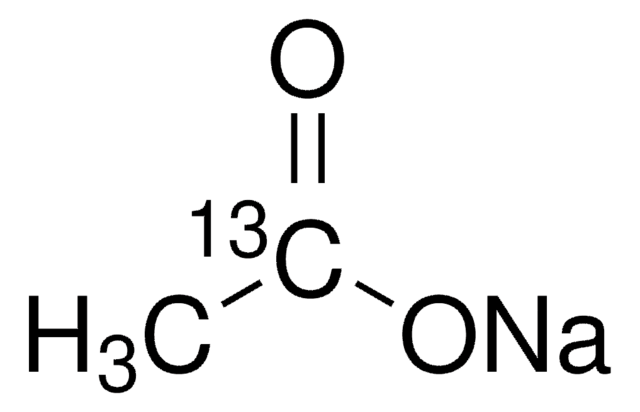
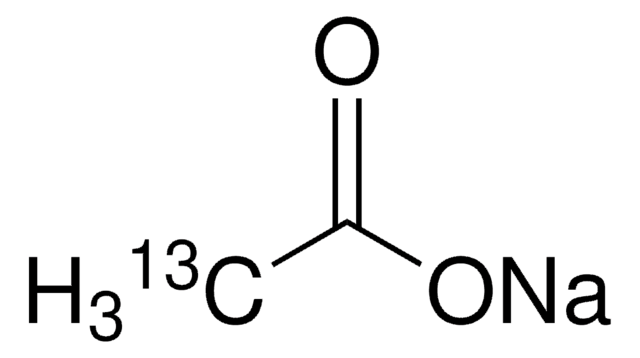
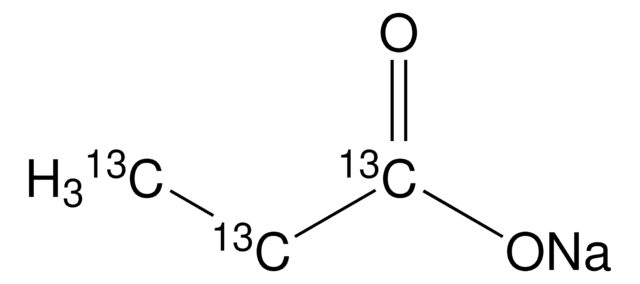
Sodium acetate-13C2
99 atom % 13C
Synonym(s):
13C Labeled acetic acid sodium salt, 13C Labeled sodium acetate, Acetic acid-13C2 sodium salt
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
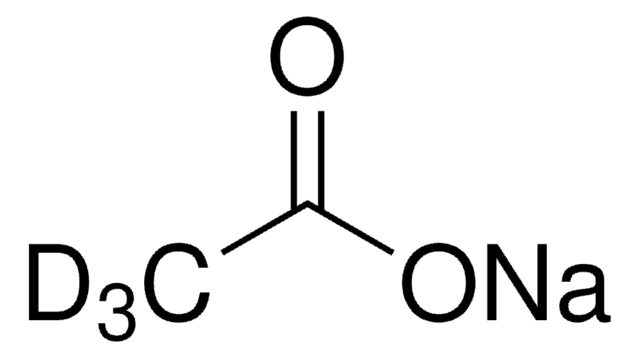
13CH313CO2Na
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
84.02
Beilstein:
4586604
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12142200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.12
Recommended Products
isotopic purity
99 atom % 13C
Quality Level
form
powder
technique(s)
bio NMR: suitable
protein expression: suitable
mp
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
mass shift
M+2
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
[Na+].[13CH3][13C]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C2H4O2.Na/c1-2(3)4;/h1H3,(H,3,4);/q;+1/p-1/i1+1,2+1;
InChI key
VMHLLURERBWHNL-AWQJXPNKSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Packaging
This product may be available from bulk stock and can be packaged on demand. For information on pricing, availability and packaging, please contact Stable Isotopes Customer Service.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Fernanda Jiménez Otero et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 87(17), e0070621-e0070621 (2021-07-01)
A strain of Geobacter sulfurreducens, an organism capable of respiring solid extracellular substrates, lacking four of five outer membrane cytochrome complexes (extABCD+ strain) grows faster and produces greater current density than the wild type grown under identical conditions. To understand
Jens V Andersen et al.
Neurobiology of disease, 148, 105198-105198 (2020-11-27)
Alzheimer's disease (AD) leads to cerebral accumulation of insoluble amyloid-β plaques causing synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death. Neurons rely on astrocyte-derived glutamine for replenishment of the amino acid neurotransmitter pools. Perturbations of astrocyte glutamine synthesis have been described in AD
Jens V Andersen et al.
Cell death & disease, 12(11), 954-954 (2021-10-18)
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an unremitting neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ) accumulation and gradual decline in cognitive function. Changes in brain energy metabolism arise in the preclinical phase of AD, suggesting an important metabolic component of early AD
Grayson L Chadwick et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(41), 20716-20724 (2019-09-25)
Metal-reducing bacteria direct electrons to their outer surfaces, where insoluble metal oxides or electrodes act as terminal electron acceptors, generating electrical current from anaerobic respiration. Geobacter sulfurreducens is a commonly enriched electricity-producing organism, forming thick conductive biofilms that magnify total
Patrizia Romani et al.
Nature cell biology, 21(3), 338-347 (2019-02-06)
Extracellular matrix (ECM) mechanical cues have powerful effects on cell proliferation, differentiation and death. Here, starting from an unbiased metabolomics approach, we identify synthesis of neutral lipids as a general response to mechanical signals delivered by cell-matrix adhesions. Extracellular physical
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service