All Photos(2)
About This Item
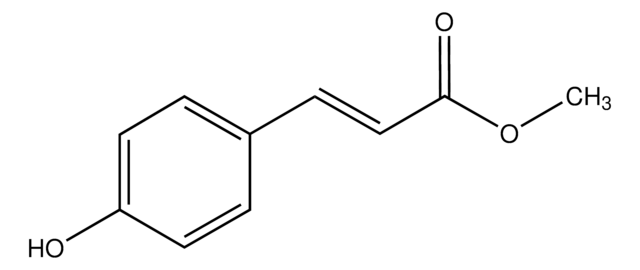
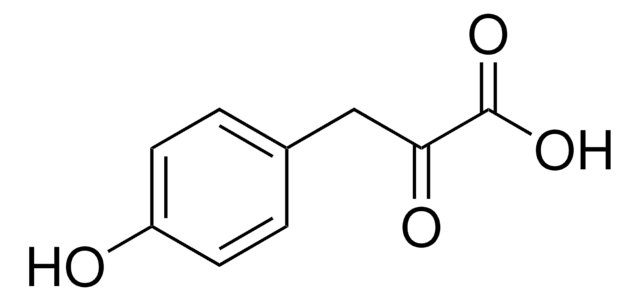
Linear Formula:
HOC6H4CH2CH2CO2CH3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
180.20
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Assay:
97%
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
bp
108 °C/11 mmHg (lit.)
mp
39-41 °C (lit.)
functional group
ester
SMILES string
COC(=O)CCc1ccc(O)cc1
InChI
1S/C10H12O3/c1-13-10(12)7-4-8-2-5-9(11)6-3-8/h2-3,5-6,11H,4,7H2,1H3
InChI key
XRAMJHXWXCMGJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate is reported to be responsible for biological nitrification inhibition in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor).
Application
Methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate may be used in the enzymatic coupling of saccharides to protein.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
113 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Ruud ter Haar et al.
Carbohydrate research, 346(8), 1005-1012 (2011-04-14)
To enable enzymatic coupling of saccharides to proteins, several di- and trisaccharides were hydroxy-arylated using anhydrous transesterification with methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate, catalyzed by potassium carbonate. This transesterification resulted in the attachment of up to 3 hydroxy-aryl units per oligosaccharide molecule, with
Hossain A K M Zakir et al.
The New phytologist, 180(2), 442-451 (2008-07-29)
Nitrification results in poor nitrogen (N) recovery and negative environmental impacts in most agricultural systems. Some plant species release secondary metabolites from their roots that inhibit nitrification, a phenomenon known as biological nitrification inhibition (BNI). Here, we attempt to characterize
Andre P Martinez et al.
Biomacromolecules, 18(6), 2000-2011 (2017-05-20)
A series of biodegradable drug delivery polymers with intrinsic multifunctionality have been designed and synthesized utilizing a polyphosphazene macromolecular engineering approach. Novel water-soluble polymers, which contain carboxylic acid and pyrrolidone moieties attached to an inorganic phosphorus-nitrogen backbone, were characterized by
Alexander K Andrianov et al.
Biomacromolecules, 19(8), 3467-3478 (2018-06-29)
Novel oppositely charged polyphosphazene polyelectrolytes containing grafted poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chains were synthesized as modular components for the assembly of biodegradable PEGylated protein delivery vehicles. These macromolecular counterparts, which contained either carboxylic acid or tertiary amino groups, were then formulated
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service