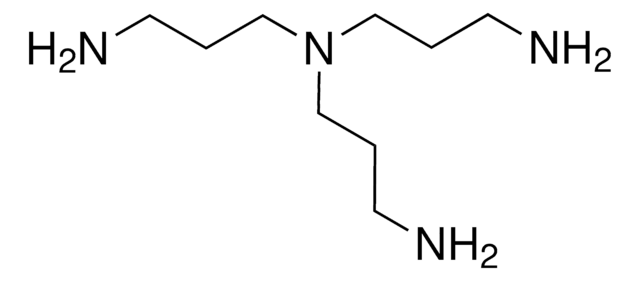
412368
PAMAM dendrimer
ethylenediamine core, generation 0.0 solution, 20 wt. % in methanol
Synonym(s):
Poly(amidoamine)
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
amino surface groups
Quality Level
form
liquid
mol wt
generation 0.0
feature
core type ethylenediamine core (2-carbon core)
concentration
20 wt. % in methanol
no. Surface Groups
4
refractive index
n20/D 1.364
bp
64.7 °C
density
0.854 g/mL at 25 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
NCCNC(=O)CCN(CCN(CCC(=O)NCCN)CCC(=O)NCCN)CCC(=O)NCCN
InChI
1S/C22H48N10O4/c23-5-9-27-19(33)1-13-31(14-2-20(34)28-10-6-24)17-18-32(15-3-21(35)29-11-7-25)16-4-22(36)30-12-8-26/h1-18,23-26H2,(H,27,33)(H,28,34)(H,29,35)(H,30,36)
InChI key
SENLDUJVTGGYIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Physical form
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Flam. Liq. 2 - STOT SE 1
Target Organs
Eyes,Central nervous system
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
49.5 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
9.7 °C - closed cup
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Replace volatile organic solvents with water due to environmental concerns, overcoming challenges in solubility.
Replace volatile organic solvents with water due to environmental concerns, overcoming challenges in solubility.
Replace volatile organic solvents with water due to environmental concerns, overcoming challenges in solubility.
Replace volatile organic solvents with water due to environmental concerns, overcoming challenges in solubility.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service