482285
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer
99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Dirhodium tetraacetate, Tetrakis(acetato)dirhodium(II)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
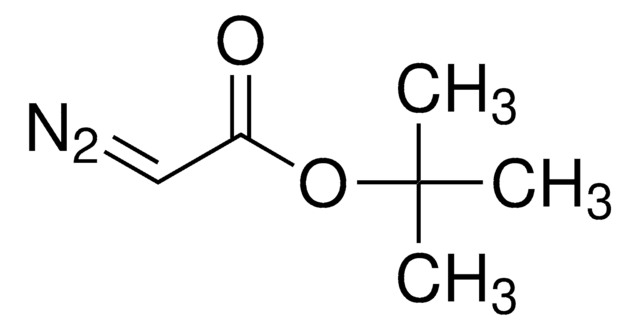
Rh2(OOCCH3)4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
441.99
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352103
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99.9% trace metals basis
form
powder
reaction suitability
reaction type: C-H Activation
reagent type: catalyst
SMILES string
CC(=O)O[Rh]OC(C)=O.CC(=O)O[Rh]OC(C)=O
InChI
1S/4C2H4O2.2Rh/c4*1-2(3)4;;/h4*1H3,(H,3,4);;/q;;;;2*+2/p-4
InChI key
SYBXSZMNKDOUCA-UHFFFAOYSA-J
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Catalyst for Rh-mediated C-H activation
Effective catalyst for ylide formation.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Rhodium carbenoid mediated C-H activation of a tertiary methyl group: an enantiospecific approach to the angular triquinanes norsilphiperfolane and norcameroonanes
Srikrishna, A.; et al.
Synlett, 16, 2343-2346 (2011)
Jaroslav V Burda et al.
Journal of inorganic biochemistry, 102(1), 53-62 (2007-08-19)
In our study, we have determined the thermodynamic behavior for the replacement reaction of one and two acetyl-ligands from the diaqua-tetrakis(mu-acetylato)dirhodium(II,II) complex by purine DNA bases. The complexes were optimized at the density functional theory (DFT) level with the B3LYP
DNA cleavage by photogenerated Rh(2)(O(2)CCH(3))(4)(H(2)O)(2)(+).
P K Fu et al.
Inorganic chemistry, 40(11), 2476-2477 (2001-05-15)
A Barnea et al.
Journal of inorganic biochemistry, 40(2), 103-110 (1990-10-01)
We have previously demonstrated that hypothalmic slices obtained from adult male rats accumulate 67Cu by two ligand-dependent, saturable processes: a high and low affinity process. To further establish the generality of these uptake processes, we defined the ligand requirements and
Vânia André et al.
Acta crystallographica. Section C, Crystal structure communications, 64(Pt 10), m345-m348 (2008-10-08)
In this paper, we compare and discuss the very different crystal structures and supramolecular arrangements obtained when using different crystallization solvents with the same organometallic moiety. The new title tetrahydrofuran (THF) solvate, [Rh(2)(C(2)H(3)O(2))(4)(C(27)H(36)N(2))(2)] x 4 C(4)H(8)O, is compared with the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service

![Bis[rhodium(α,α,α′,α′-tetramethyl-1,3-benzenedipropionic acid)] 95%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/102/178/d1171a49-0358-406b-8b32-04324dbf9c02/640/d1171a49-0358-406b-8b32-04324dbf9c02.png)