N3633
β-Naphthoflavone
≥98%
Synonym(s):
beta-Naphthoflavone, 5,6-Benzoflavone, BNF
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98%
color
off-white to yellow
mp
164-166 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O=C1C=C(Oc2ccc3ccccc3c12)c4ccccc4
InChI
1S/C19H12O2/c20-16-12-18(14-7-2-1-3-8-14)21-17-11-10-13-6-4-5-9-15(13)19(16)17/h1-12H
InChI key
OUGIDAPQYNCXRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
rat ... Gabra2(29706)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- as aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist to elucidate its effect on Cyp1A1 expression in embryos of transgenic cytochrome P450 1A1 (cyp1a) reporter zebrafish
- as AhR agonists, to treat primary normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEKs) to study about aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation by western blot analysis
- to determine its effect on the expression of dystrophin (Dp)71
- to stimulate the expression of causes recombination (Cre) recombinase and to delete the flanking alleles of locus of crossing (x) over, P1 (loxP) sequences
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Antioxidants protect biological systems from oxidative damage produced by oxygen-containing free radicals and from redoxactive transition metal ions such as iron, copper, and cadmium.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service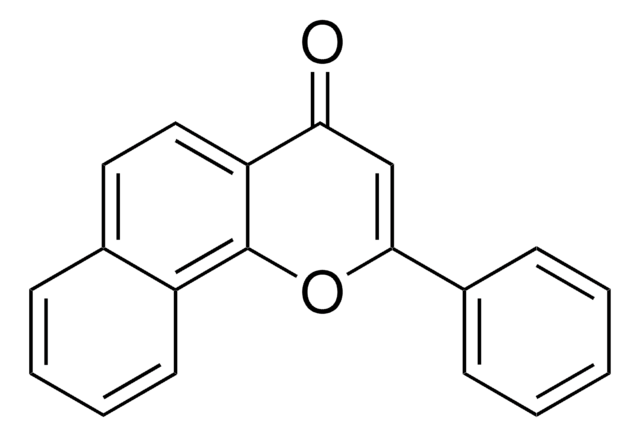

![Benzo[a]pyrene ≥96% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/253/820/be96d879-1811-46c0-8f11-612019691c2d/640/be96d879-1811-46c0-8f11-612019691c2d.png)