67028
Methylglyoxal solution
technical, ~40% in H2O
Synonym(s):
Acetylformaldehyde, Pyruvaldehyde, Pyruvic aldehyde
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
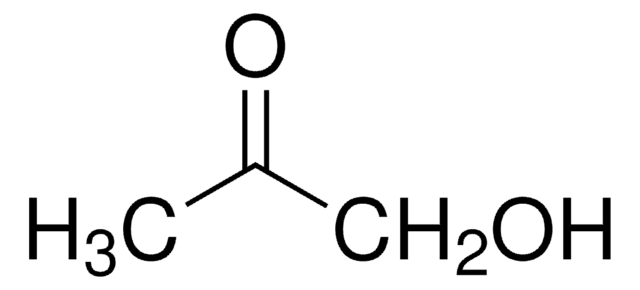
CH3COCHO
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
72.06
Beilstein:
906750
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
grade
technical
Quality Level
concentration
~40% in H2O
density
1.19 g/mL at 20 °C
functional group
aldehyde
ketone
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[H]C(=O)C(C)=O
InChI
1S/C3H4O2/c1-3(5)2-4/h2H,1H3
InChI key
AIJULSRZWUXGPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Methylglyoxal is a toxic endogenous by-product of glycolysis. It is a reactive dicarbonyl compound that promotes non-enzymatic glycation of proteins to yield irreversible advanced glycated end products, leading to the cross-linking or degradation of proteins.
Application
Methylglyoxal solution is used in cytotoxic studies.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Met. Corr. 1 - Muta. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Determination of methylglyoxal in human blood plasma using fluorescence high performance liquid chromatography after derivatization with 1, 2-diamino-4, 5-methylenedioxybenzene.
Ogasawara Y, et al.
Journal of Chromatography. B, Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1029, 102-105 (2016)
Computational and experimental exploration of the structure?activity relationships of flavonoids as potent glyoxalase?I inhibitors.
Al?Balas Q A, et al.
Drug Development Research, 79(2), 58-69 (2018)
Potential Neuroprotective and Anti-Apoptotic Properties of a Long-Lasting Stable Analog of Ghrelin: an In Vitro Study Using SH-SY5Y Cells.
Popelova A, et al.
Physiological Research, 67(2), 339-346 (2018)
Björn Kuhla et al.
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1043, 211-216 (2005-07-23)
The accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in brains with Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been implicated in the formation of insoluble deposits such as amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. AGEs are also known to activate glia, resulting in inflammation
Xiao-Yan Zou et al.
The Journal of investigative dermatology, 135(2), 589-598 (2014-09-04)
Glyoxalase I (GLO1) is a methylglyoxal detoxification enzyme being implicated in the progression of multiple malignancies. However, currently, the role of GLO1 in human nonmelanoma skin tumors remains unclear. To explore the expression of GLO1 in cutaneous neoplasms and its
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service