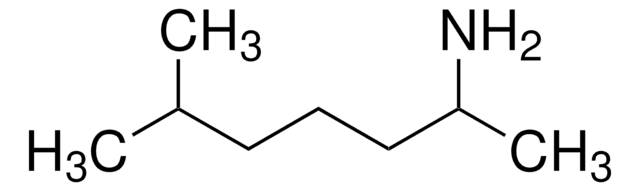
86247
Taka-Diastase from Aspergillus oryzae
powder, slightly beige, ~100 U/mg
Synonym(s):
α-Amylase from Aspergillus oryzae, Taka-Amylase A, 1,4-α-D-Glucan-glucanohydrolase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
biological source
Aspergillus sp. (A. oryzae)
Quality Level
form
powder
specific activity
~100 U/mg
color
slightly beige
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Taka-Diastase from Aspergillus oryzae has been used in thiamin extraction and conventional vitamin assay.
Unit Definition
One unit corresponds to the amount of enzyme which liberates 1 μmol maltose per minute at pH 6.0 and 25 °C (starch according to Zulkowsky, Cat. No. 85642, as substrate).
Other Notes
View more information on enzymes for complex carbohydrate analysis at www.sigma-aldrich.com/enzymeexplorer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
R B Zimbelman et al.
Journal of dairy science, 93(6), 2387-2394 (2010-05-25)
Twelve multiparous Holstein cows (145+/-9 d in milk) were randomly assigned to receive either 0 g/d of encapsulated niacin (control diet; C) or 12 g/d of encapsulated niacin (NI) and were exposed to thermoneutral (TN; 7 d) or heat stress
Thiamin fortification of bread-making flour: Retention in bread and levels in Australian commercial fortified bread varieties
Tiong S A, et al.
J. Food Compos. Anal., 38, 27-31 (2015)
Assessment of bioavailable B vitamin content in food using in vitro digestibility assay and LC-MS SIDA
Paalme T, et al.
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409(27), 6475-6484 (2017)
Jie-Lun Hu et al.
International journal of biological macromolecules, 54, 264-269 (2012-12-19)
Effects of a novel polysaccharide (PLP) from the seeds of Plantago asiatica L. on intestinal function were investigated in vitro. Results showed that PLP had notable influence on slowing down glucose diffusion and inhibiting α-amylase activity. These might help prolong
André M N Silva et al.
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 530(1), 23-31 (2012-12-19)
The study of protein damage by oxidative processes and its influence on protein activity is central to understanding the deleterious effects of oxidative stress on biological systems. This paper will focus on the study of enzyme inactivation by oxidative modifications
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service