91000
Atto 647N azide
BioReagent, suitable for fluorescence
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352125
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
product line
BioReagent
Quality Level
form
solid
mol wt
Mw 959 g/mol
manufacturer/tradename
ATTO-TEC GmbH
fluorescence
λex 644 nm; λem 661 nm
suitability
suitable for fluorescence
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
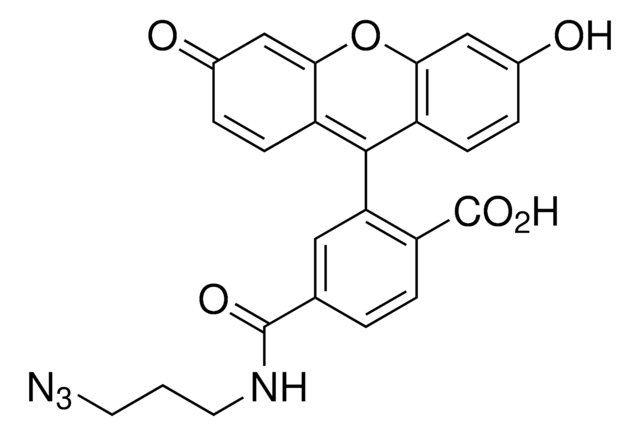
Atto 647N is a superior red-emitting label with high molecular absorption (150.000) and quantum yield (0.65) as well as sufficient stoke′s shift. Atto 647N is characterized by a high thermal and photostability. Absorption and fluorescence are independent of pH, at least in the most relevant range of pH 4 to 11. The azide modification is suitable for reactions with alkyne groups (Huisgen reaction - "Click Chemistry").
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Harpreet Singh et al.
Mitochondrion, 12(2), 230-236 (2011-10-11)
The visualization and quantification of mitochondria-associated proteins with high power microscopy methods is of particular interest to investigate protein architecture in this organelle. We report the usage of a custom-made STimulated Emission Depletion (STED) fluorescence nanoscope with ~30nm lateral resolution
Marina I Giannotti et al.
Biomacromolecules, 12(7), 2524-2533 (2011-05-25)
Nanopharmaceutics composed of a carrier and a protein have the potential to improve the activity of therapeutical proteins. Therapy for lysosomal diseases is limited by the lack of effective protein delivery systems that allow the controlled release of specific proteins
A novel nanoscopic tool by combining AFM with STED microscopy.
Harke, B., et al.
Optical Nanoscopy, 1, 3-3 (2012)
STED microscopy to monitor agglomeration of silica particles inside A549 cells.
Schubbe, S., et al.
Advanced Engineering Materials, 12, 417-422 (2010)
Volker Westphal et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 320(5873), 246-249 (2008-02-23)
We present video-rate (28 frames per second) far-field optical imaging with a focal spot size of 62 nanometers in living cells. Fluorescently labeled synaptic vesicles inside the axons of cultured neurons were recorded with stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy in
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service