A2765
Azocasein
protease substrate, chromogenic, powder
Synonym(s):
Sulfanilamide-azocasein
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Azocasein, protease substrate
biological source
bovine
Quality Level
form
powder
technique(s)
ligand binding assay: suitable
solubility
water: 5 mg/mL, clear, orange to very deep orange
ε (extinction coefficient)
≥25 at 440 nm in 0.1 M NaOH at 1%
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
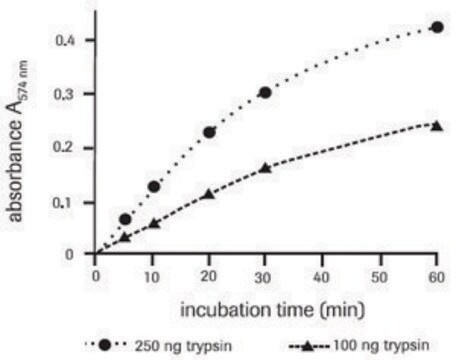
Azocasein is a chromogenic derivative of casein. Protease degrades azocasein to yield TCA-soluble azopeptides with high UV-absorbance. This azocasein assay is widely employed to estimate the protease production by bacterial fermentation on synthetic substrates from glucose and inorganic salts.
Application
Azocasein has been used as a substrate for determination of protease activity.
Azocasein is a nonspecific protease substrate. Hydrolysis of the casein releases the azo dye into the media where it is detected by absorbance at 440 nm.
Azocasein is an inflammatory agent that is used to induce amyloid A amylooidosis in experimental animals.
Linkage
View more information on azocasein protease assay at www.sigma-aldrich.com/enzymeexplorer
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Isabel Morales-Belpaire et al.
Water research, 42(17), 4449-4456 (2008-09-03)
Laboratory data on the behaviour of the pathogenic form of the prion protein (PrP(Sc)) in environmental matrices such as sewage sludge is scarce. Direct experiments with this misfolded protein require strict safety measures, pathogen class-3 facilities and costly reagents. However
Isolation and characterization of chitinolytic Streptomyces sp. MT7 and its antagonism towards wood-rotting fungi
Nagpure, A, et al.
Annals of Microbiology, 64(2), 531-541 (2014)
Yosuke Tashiro et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 191(24), 7509-7519 (2009-10-20)
The opportunistic human bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces membrane vesicles (MVs) in its surrounding environment. Several features of the P. aeruginosa MV production mechanism are still unknown. We previously observed that depletion of Opr86, which has a role in outer
Nicolas Oswaldo Gomez et al.
Molecular microbiology, 115(1), 84-98 (2020-09-09)
To overcome the metal restriction imposed by the host's nutritional immunity, pathogenic bacteria use high metal affinity molecules called metallophores. Metallophore-mediated metal uptake pathways necessitate complex cycles of synthesis, secretion, and recovery of the metallophore across the bacterial envelope. We
Hongfei Liu et al.
Protein and peptide letters, 27(11), 1102-1113 (2020-03-21)
Protein drugs have disadvantages, such as short half-lives, unstable biological activities, and low utilization efficiency. In this paper, a porous ion-responsive targeted drug delivery system was designed, combining biodegradable carriers with ion exchange technology to overcome problems for protein drug
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service