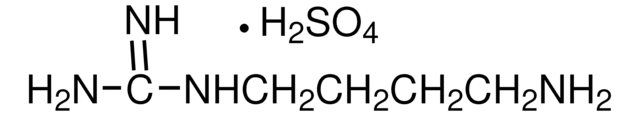A3133
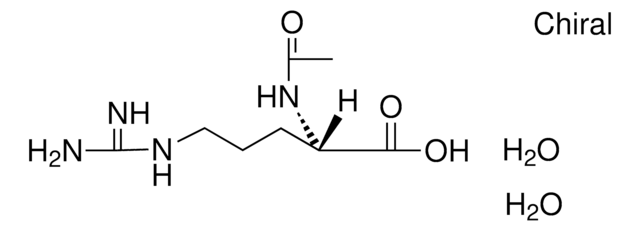
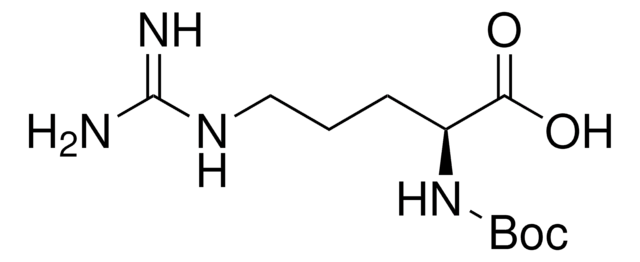
Nα-Acetyl-L-arginine
≥98% (TLC), suitable for deacetylase assays
Synonym(s):
N2-acetyl-L-alanine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C8H16N4O3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
216.24
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
eCl@ss:
32160406
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
Product Name
Nα-Acetyl-L-arginine,
Assay
≥98% (TLC)
Quality Level
form
powder
technique(s)
deacetylase assay: suitable
color
colorless to white
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
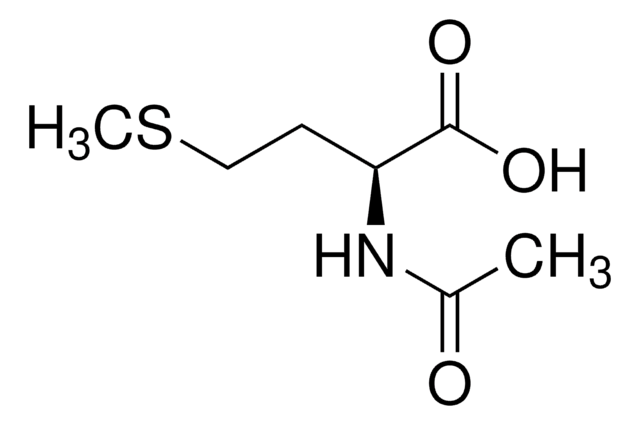
NC(NCCC[C@H](NC(C)=O)C(O)=O)=N
InChI
1S/C8H16N4O3/c1-5(13)12-6(7(14)15)3-2-4-11-8(9)10/h6H,2-4H2,1H3,(H,12,13)(H,14,15)(H4,9,10,11)/t6-/m0/s1
InChI key
SNEIUMQYRCDYCH-LURJTMIESA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
T W Lo et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 269(51), 32299-32305 (1994-12-23)
The physiological alpha-oxoaldehyde methylglyoxal binds and modifies arginine, lysine, and cysteine residues in proteins. The kinetics and mechanism of these reactions were investigated with N alpha-acetylamino acids and bovine serum albumin at pH 7.4 and 37 degrees C. The reaction
Binding of methylglyoxal to albumin and formation of fluorescent adducts. Inhibition by arginine, N-alpha-acetylarginine and aminoguanidine.
T Selwood et al.
Biochemical Society transactions, 21(2), 170S-170S (1993-05-01)
Daniela Balz et al.
International journal of developmental neuroscience : the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience, 21(2), 75-82 (2003-03-05)
Tissue accumulation of arginine (Arg), N-acetylarginine (NA), argininic acid (AA) and homoarginine (HA) occurs in hyperargininemia, an inborn error of the urea cycle. In the present study, we investigated the in vitro effects of Arg, NA, AA and HA on
A T Wyse et al.
Brain research, 923(1-2), 50-57 (2001-12-18)
Hyperargininemia is a metabolic disorder biochemically characterized by tissue accumulation of arginine and other guanidino compounds. Convulsions, lethargy and psychomotor delay or cognitive deterioration are predominant clinical features of this disease. Although neurologic symptoms predominate in this disorder, their pathophysiology
P De Deyn et al.
Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry, 157(2), 143-150 (1986-06-15)
The concentrations of guanidino compounds in blood are raised in uraemic patients and may have toxic effects. The concentrations of 13 guanidino compounds in serum were measured in 29 patients with chronic renal failure treated by chronic intermittent haemodialysis using
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service