G4252
Glyoxalase I from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Grade IV, buffered aqueous glycerol solution, ≥400 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
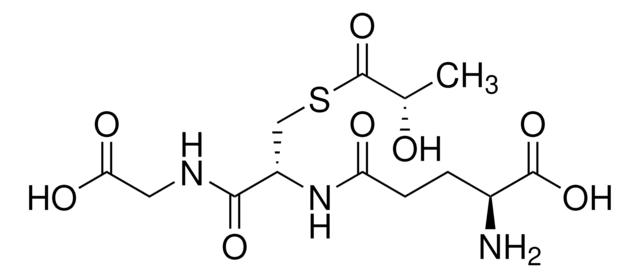
S-Lactoyl-glutathione methylglyoxal-lyase (isomerizing)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
type
Grade IV
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
specific activity
≥400 units/mg protein
foreign activity
glyoxalase II ≤1%
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Glyoxalase detoxification system consists of glyoxalase (GLO)-I and GLO-II. GLO-I is a cytosolic, 42 kDa, dimeric Zn2+ metalloenzyme.
Application
Glyoxalase I from Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been used as a standard in Glyoxalase I assay for C. dilatata females and brooded encapsulated embryos. It has also been used as a standard for calibration curve generation for quantifying glyoxalase I from brain tissues and cerebral microvessels.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Glyoxalase I is universally expressed and involved in the protection against cellular damage due to cytotoxic metabolites such as advanced glycation end products (AGEs). It is an integral component of the detoxification system, catalyzing the conversion of reactive, acyclic a-oxoaldehydes into the corresponding a-hydroxyacids in a glutathione-dependent manner.
Unit Definition
One unit will form 1.0 μmole of S-lactoylglutathione from methylglyoxal and reduced glutathione per min at pH 6.6 at 25 °C.
Physical form
Solution in 50% glycerol, 0.4 M (NH4)2SO4 and 0.002 M KH2PO4 pH 6.5
Analysis Note
Protein determined by biuret.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
The mechanism of action of glyoxalase.
E RACKER
The Journal of biological chemistry, 190(2), 685-696 (1951-06-01)
An enzyme concerned with the formation of hydroxy acids from ketonic aldehydes
H.D. Dakin & H.W. Dudley
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 14, 155-157 (1913)
Ravi Gupta et al.
Journal of proteome research, 11(5), 2684-2696 (2012-04-11)
Plants' distribution and productivity are adversely affected by low temperature (LT) stress. LT induced proteins were analyzed by 2-DE-nano-LC-MS/MS in shoot secretome of Hippophae rhamnoides (seabuckthorn), a Himalayan wonder shrub. Seedlings were subjected to direct freezing stress (-5 °C), cold
Miriam Urscher et al.
The FEBS journal, 279(14), 2568-2578 (2012-05-23)
Glucose consumption and therefore methylglyoxal production of human erythrocytes increase significantly upon infection with malaria parasites. The glyoxalase systems of the host-parasite unit cope with this metabolic challenge by catalyzing the removal of harmful methylglyoxal. Thus, glyoxalase 1 from the
Xuming Jia et al.
PloS one, 7(5), e36610-e36610 (2012-05-19)
Methylglyoxal (MG) is a highly reactive metabolite physiologically presented in all biological systems. The effects of MG on diabetes and hypertension have been long recognized. In the present study, we investigated the potential role of MG in obesity, one of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service