L8292
Lipoprotein, low density from human plasma
lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
β-Lipoprotein, LDL, Low density lipoprotein
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human plasma
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
packaging
vial of ~5 mg protein
technique(s)
cell culture | stem cell: suitable
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
human ... APOA1(335)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- in evaluating its anti-Langerhans cells (LC) differentiation activity in monocyte-derived Langerhans cells (MDLCs)
- in the preparation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)
- as a lipoprotein standard in quantifying embryonic cerebrospinal fluid (eCSF) from HH23 embryos by lipid staining
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical properties
Preparation Note
Disclaimer
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
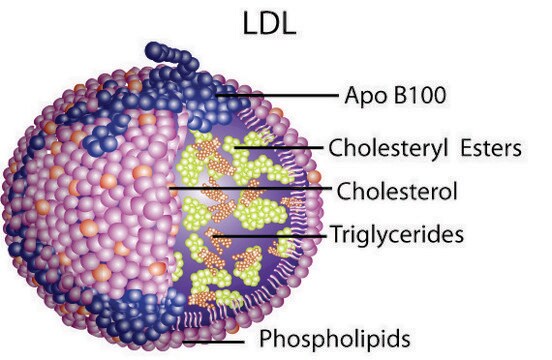
Lipoproteins package cholesterol for transport in plasma, essential for lipid transport and cellular function in the body.
Lipoproteins package cholesterol for transport in plasma, essential for lipid transport and cellular function in the body.
Lipoproteins package cholesterol for transport in plasma, essential for lipid transport and cellular function in the body.
Lipoproteins package cholesterol for transport in plasma, essential for lipid transport and cellular function in the body.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service