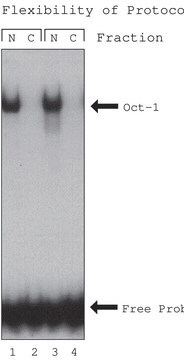
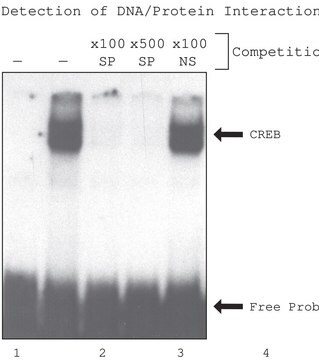
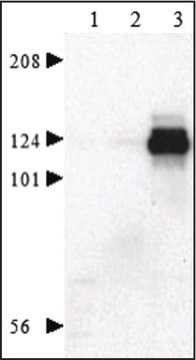
NUC101
Nuclei Isolation Kit: Nuclei EZ Prep
sufficient for 25 nuclei preparations (~1-10×107 cells/preparation)
Synonym(s):
Rapid mammalian nuclei isolation kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 25 nuclei preparations (~1-10×107 cells/preparation)
Quality Level
shelf life
1 yr at 2‑8 °C
packaging
pkg of 1 kit
application(s)
cell analysis
foreign activity
nuclease and protease, free
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Other Notes
related product
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Centrifugation separates organelles based on size, shape, and density, facilitating subcellular fractionation across various samples.
Centrifugation separates organelles based on size, shape, and density, facilitating subcellular fractionation across various samples.
Centrifugation separates organelles based on size, shape, and density, facilitating subcellular fractionation across various samples.
Centrifugation separates organelles based on size, shape, and density, facilitating subcellular fractionation across various samples.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service