X1126
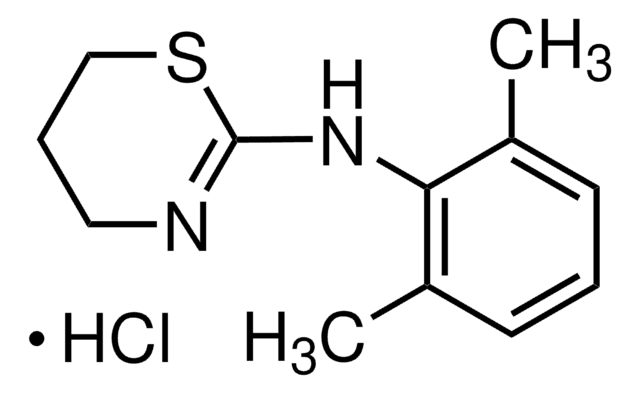
Xylazine
≥99%
Synonym(s):
2-(2,6-Dimethylphenylamino)-5,6-dihydro-4H-thiazine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C12H16N2S
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
220.33
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99%
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cc1cccc(C)c1NC2=NCCCS2
InChI
1S/C12H16N2S/c1-9-5-3-6-10(2)11(9)14-12-13-7-4-8-15-12/h3,5-6H,4,7-8H2,1-2H3,(H,13,14)
InChI key
BPICBUSOMSTKRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Xylazine is soluble in methanol (50 mg/ml), yielding a clear, colorless solution. It is also soluble in dilute HCl acid and in chloroform. Xylazine is practically insoluble in water and in alkali solutions.
Application
Xylazine has been used to anaesthetise experimental animals.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Xylazine when used along with ketamine is considered to be a potent and safe anaesthetic in experimental animal. It is known to elevate the hepatic release of glucose, which aggravates to hyperglycemia.
α2-adrenoceptor agonist, sedative, muscle relaxant.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Acute reversible cataract induced by xylazine and by ketamine-xylazine anesthesia in rats and mice
Calderone L, et al.
Experimental Eye Research, 42(4), 331-337 (1986)
MIND model for triple-negative breast cancer in syngeneic mice for quick and sequential progression analysis of lung metastasis
Ghosh A, et al.
PLoS ONE, 13(5), e0198143-e0198143 (2018)
Lactobacillus casei addition to a repletion diet-induced early normalisation of cytokine profils during a pneumococcal infection in malnourished mice
Salva S, et al.
Food and agricultural immunology, 19(3), 195-211 (2008)
Imaging of rat optic nerve axons in vivo
Koch JC, et al.
Nature Protocols, 6(12), 1887-1887 (2011)
Hannah T Nickles et al.
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 307(1), L27-L37 (2014-05-13)
The pathogenesis of ventilator-induced lung injury has predominantly been attributed to overdistension or mechanical opening and collapse of alveoli, whereas mechanical strain on the airways is rarely taken into consideration. Here, we hypothesized that mechanical ventilation may cause significant airway
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service