1448956
USP
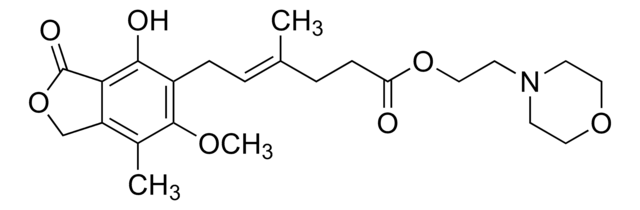
Mycophenolate mofetil
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
Synonym(s):
(4E)-6-(1,3-Dihydro-4-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranyl)-4-methyl-4-hexenoic acid 2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl ester, RS 61443, TM-MMF
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
pharmaceutical primary standard
API family
mycophenolate
manufacturer/tradename
USP
application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
format
neat
storage temp.
15-25°C
SMILES string
COc1c(C)c2COC(=O)c2c(O)c1C\C=C(/C)CCC(=O)OCCN3CCOCC3
InChI
1S/C23H31NO7/c1-15(5-7-19(25)30-13-10-24-8-11-29-12-9-24)4-6-17-21(26)20-18(14-31-23(20)27)16(2)22(17)28-3/h4,26H,5-14H2,1-3H3/b15-4+
InChI key
RTGDFNSFWBGLEC-SYZQJQIISA-N
Gene Information
human ... IMPDH1(3614) , IMPDH2(3615)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Biochem/physiol Actions
Analysis Note
Other Notes
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Repr. 1B - STOT RE 1
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service