General description
In SDS gels, the product reacts with both Regan and Nagao isozymes of human placental alkaline phosphatase (hPLAP, 130 kDa, 67/130 kDa). By RIA, the antibody binds to hPLAP with an affinity constant of 5 × 109 LM-1. It does not react with PLAP-like enzymes.
Monoclonal Anti-Human Placental Alkaline Phosphatase (mouse IgG2a isotype) is derived from the 8B6 hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from immunized BALB/c mice. Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) is a broad and general term associated with non-specific phosphomonoesterases, with optimal activity at alkaline pH. Human placental alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1; hPLAP), an isoenzyme of the AP group of enzymes, is ordinarily synthesized in the placental syncytiotrophoblast, becoming detectable in maternal circulation after the twelfth week of pregnancy. Small amounts of hPLAP are also found in the endocervix, fallopian tubes and lung. Very small amounts of heat-stable AP resembling hPLAP (hPLAP-like AP) are expressed in the testis, thymus and in rare colon epithelial cells.
Immunogen
Human epidermoid carcinoma cell line expressing placental alkaline phosphatase.
Application
Anti-Alkaline phosphatase human placental antibody coupled to agarose was packed in a column and used to purify alkaline-phosphatase conjugated FGF receptor out of conditioned media from COS-7 cells. Column was washed with 1M NaCl.
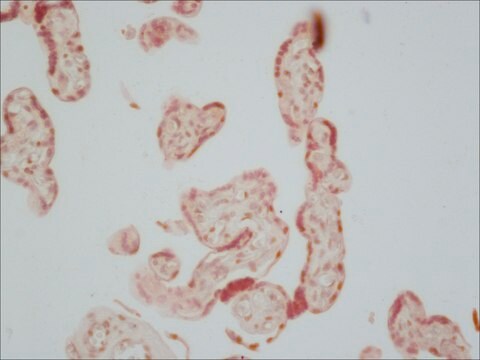
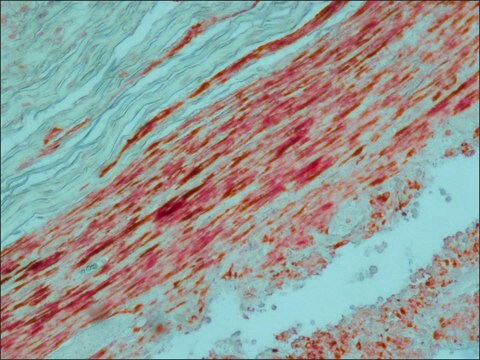
Cultured pancreatic islet cells were fixed with cold 4% paraformaldhyde at room temperature for 10 minutes and incubated with mouse monoclonal anti-Alkaline Phosphatase, Human Placental antibody at 1:500. Mouse monoclonal anti-Alkaline Phosphatase, Human Placental antibody was used to detect a unique molecular probe that consisted of the FGFR extracellular domain expressed as a chimera with human PLAP.
This immunoadsorbant may be used to purify fusion proteins produced using vectors expressing the hPLAP gene. Suitable for affinity purification and immunoprecipitation procedures of human placental alkaline phosphatase either natural or recombinant.It is alsu used in western blotting.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Alkaline phosphatases are non-specific phosphomonoesterases that function optimally at alkaline pH. Placental alkaline phosphatase differs from the alkaline phosphatases of bone, liver and kidney, in the hydrolysis rate of various phosphate-based substrates, and also in its degree of inhibition by L-phenylalanine and L-homoarginine or levamisole. Human Placental Alkaline Phosphatase (hPLAP) has been studied as a potential tumor marker.
The human placental alkaline phosphatase (hPLAP and hPLAP-like AP) is present in the sera and tumor tissue of patients suffering from various types of cancer. Despite the continued interest in hPLAP as a potential tumor marker, it has not been widely used in the routine clinical laboratory, mainly because of the low overall specificity attained by methodologies such as heat-inactivation and sensitivity to L-phenylalanine.
Physical form
Suspension in 0.1 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Preparation Note
Prepared using purified antibody coupled to cyanogen bromide-activated agarose.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.