RAB0147
Human DPPIV / CD26 ELISA Kit
for serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant and urine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41116158
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
species reactivity
human
packaging
kit of 96 wells (12 strips x 8 wells)
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
capture ELISA: suitable
input
sample type serum
sample type cell culture supernatant(s)
sample type plasma
sample type urine
assay range
inter-assay cv: <12%
intra-assay cv: <10%
sensitivity: 25 pg/mL
standard curve range: 32.77-8000 pg/mL
detection method
colorimetric
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
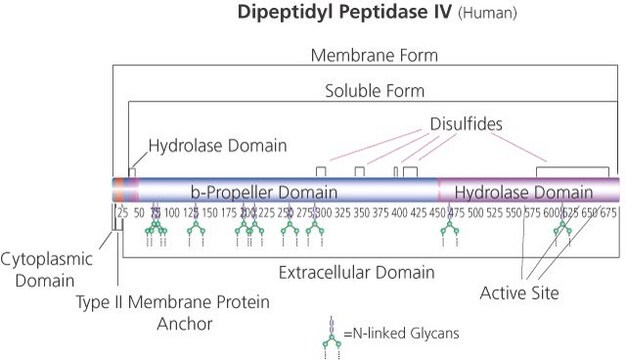
Gene Information
human ... DPP4(1803)
General description
The Human CD26 (also known as DPPIV) ELISA (Enzyme- Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of human CD26 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine.
Immunogen
Recombinant Human CD26
Application
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPPIV), also known as CD26 (cluster of differentiation 26), is localized on T- cell surface and interacts with adenosine deaminase (ADA), collagen and CD459. It plays a vital role in T cell co-stimulation, cell-to-cell adhesion, and in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Deletion of the DPPIV gene alters carbohydrate metabolism which in turn leads to mental retardation and hypotonia. Abnormal expression of DPPIV is observed during liver regeneration, human cirrhosis and liver tumorigenesis. DPPIV level is reduced in serum of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients, hence, this protein has potential as a serologic marker for screening COPD. DPP4 functions as a serine protease enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of dipeptides from peptides containing proline or alanine residues. IL-13 induced DPPIV expression is upregulated in bronchial epithelial cells (BECs) and this expression might contribute to the development of asthmatic airway inflammation, cell proliferation and fibronectin (FN) production. This protein is a promising biomarker and therapeutic target for asthma.
Other Notes
A sample Certificate of Analysis is available for this product.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Kit Components Also Available Separately
Product No.
Description
SDS
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Met. Corr. 1
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Xiao-Yue Chang et al.
The American journal of the medical sciences, 351(3), 244-252 (2016-03-20)
The purpose of this study is to explore the correlation between serum dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at its various disease states, analyze its applications in the prediction and diagnosis of COPD and test the
Taichi Shiobara et al.
Respiratory research, 17, 28-28 (2016-03-16)
Type 2 helper T-cell cytokines including IL-13 play a central role in the pathogenesis of bronchial asthma (BA). During the course of our research, our attention was drawn to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) as one of the molecules that were induced
Orazio Palumbo et al.
Molecular cytogenetics, 5(1), 1-1 (2012-01-05)
Chromosomal imbalances, recognized as the major cause of mental retardation, are often due to submicroscopic deletions or duplications not evidenced by conventional cytogenetic methods. To date, interstitial deletion of long arm of chromosome 2 have been reported for more than
Molecular analyses of human and rat dipeptidyl peptidase IV.
C A Abbott et al.
Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 421, 161-169 (1997-01-01)
C A Abbott et al.
Immunogenetics, 40(5), 331-338 (1994-01-01)
CD26 is a lymphocyte cell surface antigen which is increased during T-cell activation and is also expressed in other tissues. It is an atypical serine protease belonging to the prolyl oligopeptidase family. CD26 has been implicated in a variety of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service