S2014
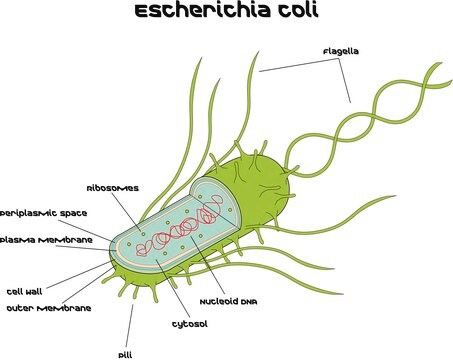
Staphylococcus aureus
buffered aqueous suspension, Wood 46 strain
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.81
Recommended Products
biological source
Staphylococcus aureus
Quality Level
sterility
Not processed or packaged aseptically
form
buffered aqueous suspension
composition
Cell suspension, ~10% wet weight/volume
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Staphylococcus aureus Wood 46 is protein A deficient and spa negative. It shares 98% to 99% genome identity with S.aureus and shows a lower surface expression of cell wall-associated protein A.
Application
(Not intended for use as a starter culture.)
Staphylococcus aureus has been used:
- to mimic infection and induce fever in Pekin duck
- to test its effect on hemocyte morphology in hemolymph samples from beetle Tenebrio molitor larva
- in the antibacterial activity and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) assay with gedunin and 7-deacetoxy-7αhydroxygedunin potassium salt
Wood 46, a non-protein A producing S. aureus strain, prepared by the same method as P7155 (Protein A, crude cell suspension-Cowan strain), may be used as a control in protein A-immunoglobulin binding studies.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Staphylococcus aureus Wood 46 displays reduced virulence compared to the S. aureus. This isolate is useful in understanding protein A role in pathogenesis and virulence.
Physical form
Formalin-fixed crude cell suspension of essentially non-viable S. aureus (Wood 46 strain) in 0.05 M potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, containing 0.2% sodium azide
Preparation Note
Produced in pure culture.
Analysis Note
This strain binds less than 10% of the rabbit IgG bound by P 7155 as assayed by a modification of the method of Kessler.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
S W Kessler
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 117(5 Pt 1), 1482-1490 (1976-11-01)
Procedures are detailed for the rapid isolation of representative cell membrane antigens with protein A-bearing staphylococci as an adsorbent for IgG antibodies complexed with the antigens. Cell surface membrane proteins were radioiodinated and solubilized in nonionic detergent. Specific antisera were
M Marais et al.
Poultry science, 90(6), 1234-1238 (2011-05-21)
Poultry, like mammals and other birds, develop fever when exposed to compounds from gram-negative bacteria. Mammals also develop fever when exposed to the constituents of viruses or gram-positive bacteria, and the fevers stimulated by these different pathogenic classes have discrete
G Kronvall et al.
Infection and immunity, 3(1), 10-15 (1971-01-01)
Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus can be detected on cell walls of intact bacteria by use of radioactively labeled myeloma globulin. Of 156 strains of S. aureus, 141 (90%) contained protein A. None of 47 S. epidermidis strains was positive
Synthetic modification of gedunin and comparative antibacterial activity of gedunin and 7-deacetoxy-7alpha-hydroxygedunin potassium salt
Okhale SE, et al.
African Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry, 6(14), 183-189 (2012)
Manasi Balachandran et al.
PloS one, 12(8), e0183913-e0183913 (2017-09-01)
Protein A in Staphylococcus aureus is encoded by the spa (staphylococcal protein A) gene and binds to immunoglobulin (Ig). The S. aureus strain Wood 46 has been variously reported as protein A-deficient and/or spa negative and used as a control
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service