S5639
Superoxide Dismutase from Escherichia coli
lyophilized powder, ≥1,000 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
SOD, Superoxide: superoxide oxidoreductase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized powder
Quality Level
specific activity
≥1,000 units/mg protein
mol wt
39.5 kDa
composition
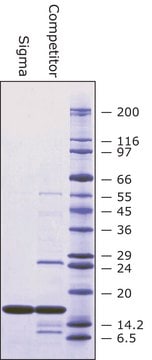
Protein, ≥70% biuret
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
Escherichia coli CFT073 ... sodA(1040208) , sodB(1036179) , sodC(1036143)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
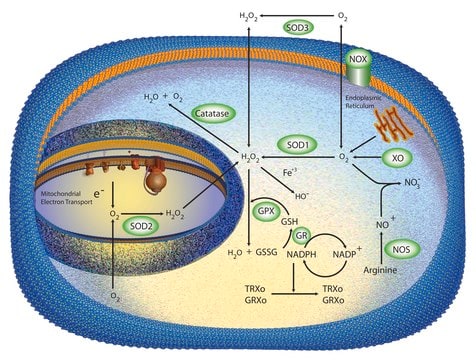
Superoxide dismutases are a group of low molecular weight metalloproteins present in all aerobic cells of plants, animals and micro-organisms. They provide protection against damaging reactions with the superoxide radical anion (O2-) by catalyzing its disproportionation into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. The direct electron transfer of superoxide dismutases can be efficiently promoted by a self-assembled monolayer of 3-mercaptopropionic acid confined on a gold electrode.
Application
Superoxide dismutase from Escherichia coli has been used in a study to determine that anion binding properties of reduced and oxidized iron-containing superoxide dismutase reveal no requirement for tyrosine 34. Superoxide dismutase from Escherichia coli has also been used in a study to demonstrate that molecular dynamics simulation and limited proteolysis are complementary and specific tools to identify flexible sites in proteins.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide radicals to hydrogen peroxide and molecular oxygen. Plays a critical role in the defense of cells against the toxic effects of oxygen radicals. Competes with nitric oxide (NO) for superoxide anion (which reacts with NO to form peroxynitrite), thereby SOD promotes the activity of NO. SOD has also been shown to suppress apoptosis in cultured rat ovarian follicles, neural cell lines, and transgenic mice.
Other Notes
Manganese-containing enzyme
Unit Definition
One unit will inhibit reduction of cytochrome c by 50% in a coupled system with xanthine oxidase at pH 7.8 at 25 °C in a 3.0 mL reaction volume. Xanthine oxidase concentration should produce an initial ΔA550 of 0.025 ± 0.005 per min.
Physical form
Contains Tris buffer salts
Analysis Note
For assay method, see McCord, J.M. and Fridovich, I., J. Biol. Chem., 244, 6049 (1969).
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Yoshikazu Kawai et al.
Nature communications, 14(1), 4123-4123 (2023-07-12)
Inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis by antibiotics such as β-lactams is thought to cause explosive lysis through loss of cell wall integrity. However, recent studies on a wide range of bacteria have suggested that these antibiotics also perturb central
Anne-Frances Miller et al.
Biochemistry, 44(16), 5969-5981 (2005-04-20)
We report the first spectroscopic observation of substrate analogue binding to the reduced state of iron superoxide dismutase from Escherichia coli (Fe(2+)SOD) and demonstrate that the pH dependence reflects inhibition of anion binding by ionized Tyr34, not loss of a
M Falconi et al.
Proteins, 47(4), 513-520 (2002-05-10)
Limited proteolysis by trypsin of monomeric Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase from Escherichia coli induces a specific cleavage of the polypeptide chain at the level of Lys60 located in the S-S subloop of loop 6,5 where, when compared to the eukaryotic enzyme
U Wendling et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 164(5), 2711-2717 (2000-02-29)
Immunization with Mycobacterium tuberculosis heat shock protein (hsp) 60 has been shown to protect rats from experimental arthritis. Previously, the protection-inducing capacity was shown to reside in the evolutionary conserved parts of the molecule. Now we have studied the nature
Yang Tian et al.
Analytical chemistry, 76(14), 4162-4168 (2004-07-16)
In this article, the electrochemical properties and electrocatalytic activity of three kinds of superoxide dismutases (SODs), that is, bovine erythrocyte copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD), iron superoxide dismutase from Escherichia coli (Fe-SOD), and manganese superoxide dismutase from E. coli (Mn-SOD), in
Protocols
Enzymatic Assay of Superoxide Dismutase
Separation of Superoxide dismutase
Chromatograms
application for HPLCOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service