126535
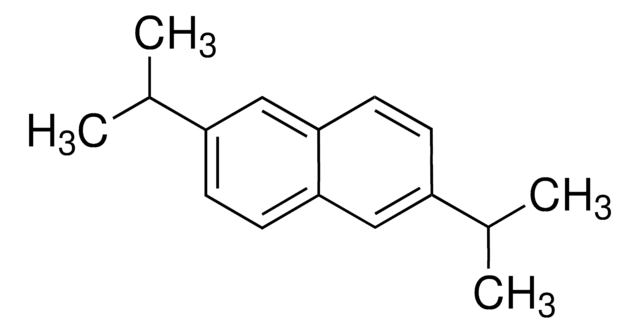
2,6-Dimethylnaphthalene
99%
Synonym(s):
2,6-Dimethylnaphthalene
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C10H6(CH3)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
156.22
Beilstein:
1903544
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Assay
99%
bp
262 °C (lit.)
mp
106-110 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Cc1ccc2cc(C)ccc2c1
InChI
1S/C12H12/c1-9-3-5-12-8-10(2)4-6-11(12)7-9/h3-8H,1-2H3
InChI key
YGYNBBAUIYTWBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... CYP1A2(1544)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
2,6-dimethylnaphthalene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon available in the water bodies and can be determined by gas chromatography with flame-ionization.
Application
2,6-Dimethylnaphthalene hs been used as a substrate in intramolecular isotope effect experiments to compare substrate dynamics in CYP2E1 and CYP2A6.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
N Miyachi et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 59(5), 1504-1506 (1993-05-01)
Three bacterial strains, identified as Alcaligenes sp. strain D-59 and Pseudomonas sp. strains D-87 and D-186, capable of growing on 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene (2,6-DMN) as the sole source of carbon and energy were isolated from soil samples. 2,6-Naphthalene dicarboxylic acid was formed
Dietary accumulation of dimethylnaphthalene by the grass shrimp Palaemonetes pugio under stable and fluctuating temperatures.
T M Dillon
Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology, 28(2), 149-153 (1982-02-01)
Effect of Aroclor 1254 on the biological fate of 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch).
T K Collier et al.
Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology, 34(1), 114-120 (1985-01-01)
Z A Shamsuddin et al.
Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals, 14(6), 724-732 (1986-11-01)
Metabolism of the environmental contaminant 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene (2,6-DMN) by rat liver microsomes and an NADPH-regenerating system led to the formation of three ring oxidation metabolites--2,6-dimethyl-3-naphthol, 2,6-dimethyl-3,4-naphthoquinone, and 3,4-dihydro-3,4-dihydroxy-2,6-dimethylnaphthalene--and one side chain oxidation metabolite--2-hydroxymethyl-6-methylnaphthalene. In addition, one metabolite remained unidentified. Pretreatment of
E A Barnsley
Applied and environmental microbiology, 54(2), 428-433 (1988-02-01)
Flavobacteria that were able to grow on 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene (2,6-DMN) were isolated from soil. Most were able to oxidize a broad range of aromatic hydrocarbons after growth on 2,6-DMN at rates comparable to that of the oxidation of 2,6-DMN itself. One
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service