129658
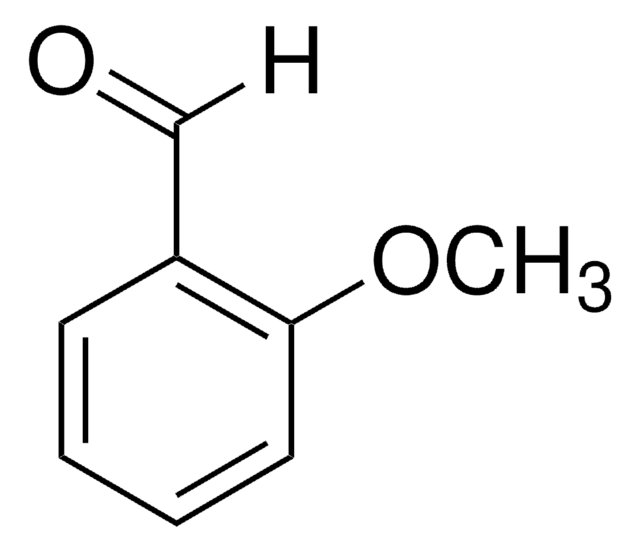
m-Anisaldehyde
97%
Synonym(s):
3-Methoxybenzaldehyde
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3OC6H4CHO
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
136.15
Beilstein:
606013
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
form
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.553 (lit.)
bp
143 °C/50 mmHg (lit.)
density
1.117 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
functional group
aldehyde
SMILES string
[H]C(=O)c1cccc(OC)c1
InChI
1S/C8H8O2/c1-10-8-4-2-3-7(5-8)6-9/h2-6H,1H3
InChI key
WMPDAIZRQDCGFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
m-Anisaldehyde has significant antifungal activity against Candida sp., including the azole-resistant strains.
m-Anisaldehyde is a class of benzaldehyde, used as a potent antifungal agent and as the starting material for complex aromatic compounds.
m-Anisaldehyde is a class of benzaldehyde, used as a potent antifungal agent and as the starting material for complex aromatic compounds.
Application
m-Anisaldehyde was used as an eluent for mono-13C isotopomers of vanillin in normal phase silica gel chromatography. It was also used as an inhibitor of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) metabolism.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
113 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Inhibition of metabolism of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone by dietary benzaldehydes.
M A Morse et al.
Cancer letters, 97(2), 255-261 (1995-11-06)
As part of a routine screening assay, benzaldehyde was found to inhibit 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) metabolism. Consequently, the effects of benzaldehyde and several structurally related compounds on NNK metabolism were examined in murine hepatic and pulmonary microsomes. All test compounds inhibited
Structural and spectroscopic (UV--Vis, IR, Raman, and NMR) characteristics of anisaldehydes that are flavoring food additives: A density functional study in comparison with experiments
Altun, et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1128, 590-605 (2017)
Retention of sparingly soluble volatile compounds during the freeze drying of model solutions
Smyrl,et al.
Journal of Food Process Engineering, 2, 151-170 (1978)
Eliot P Botosoa et al.
Journal of chromatography. A, 1216(42), 7043-7048 (2009-09-15)
Quantitative isotopic (13)C NMR at natural abundance has been used to determine the site-by-site (13)C/(12)C ratios in vanillin and a number of related compounds eluted from silica gel chromatography columns under similar conditions. Head-to-tail isotope fractionation is observed in all
Sheikh Shreaz et al.
Microbial pathogenesis, 51(4), 277-284 (2011-06-15)
Attention has been drawn to evaluate the antifungal activity of p-anisaldehyde (1), o-anisaldehyde (2) and m-anisaldehyde (3). To put forward this approach, antifungal activity has been assessed in thirty six fluconazole-sensitive and eleven fluconazole-resistant Candida isolates. Growth and sensitivity of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service