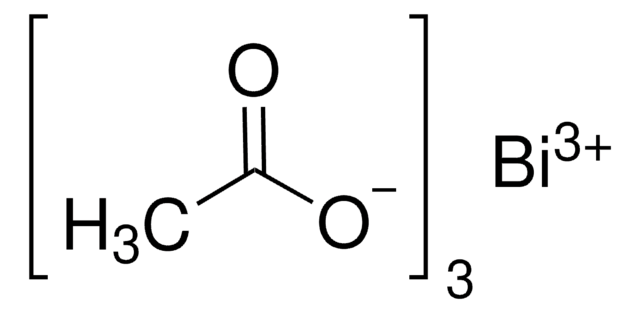
86370
Tellurium dioxide
≥97.0%
Synonym(s):
Telluria, Tellurium oxide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
TeO2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
159.60
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352303
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥97.0%
form
powder
mp
733 °C (lit.)
density
5.67 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
O=[Te]=O
InChI
1S/O2Te/c1-3-2
InChI key
LAJZODKXOMJMPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Tellurium dioxide (TeO2) is a ceramic material that can be used as a semiconducting oxide. It has a wide band gap and high mobility as determined by density functional theory (DFT) calculations. In bulk quantity, it exists in two polymorphs which include tetragonal α-TeO2 and orthorhombic β-TeO2.
Application
TeO2 can be potentially used in medical imaging and industrial monitoring processes.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Lact. - Repr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Ultrathin tellurium dioxide: emerging direct bandgap semiconductor with high-mobility transport anisotropy
Guo S, et al.
Nanoscale, 10(18), 8397-8403 (2018)
Gamma radiation-induced changes in the electrical and optical properties of tellurium dioxide thin films
Arshak K and Korostynska O
IEEE Sensors Journal, 3(6), 717-721 (2003)
Sankha Chattopadhyay et al.
Applied radiation and isotopes : including data, instrumentation and methods for use in agriculture, industry and medicine, 68(10), 1967-1969 (2010-05-18)
A simple and inexpensive ion-exchange chromatography method for the separation of medically useful no-carrier-added (nca) iodine radionuclides from bulk amounts of irradiated tellurium dioxide (TeO(2)) target was developed and tested using (131)I. The radiochemical separation was performed using a very
Sankha Chattopadhyay et al.
Applied radiation and isotopes : including data, instrumentation and methods for use in agriculture, industry and medicine, 67(10), 1748-1750 (2009-05-05)
A simple and inexpensive method for the separation of medically useful no-carrier-added (nca) iodine radionuclides from bulk amounts of irradiated tellurium dioxide (TeO(2)) target was developed. The beta(-) emitting (131)I radionuclide, produced by the decay of (131)Te through the (nat)Te(n
Garima Tripathi et al.
Spectrochimica acta. Part A, Molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy, 71(2), 486-489 (2008-03-14)
The energy transfer in Er3+: Sm3+ codoped binary TeO2-Li2O (TLO) glass has been studied using 532 nm laser radiation on the basis of fluorescence intensity and the lifetime measurements. It is observed that the trace of erbium ion can be
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service