All Photos(1)
About This Item
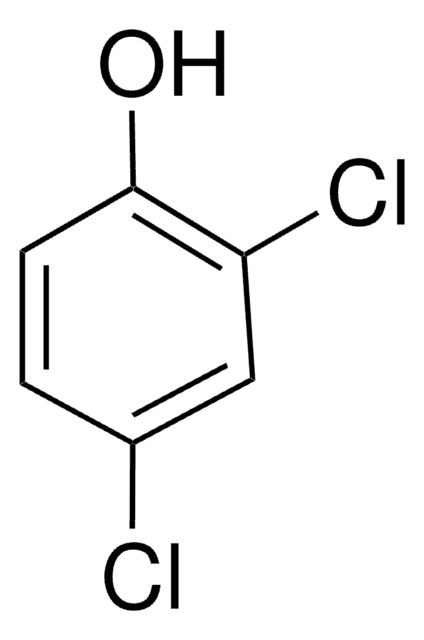
Linear Formula:
Cl2C6H3OH
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
163.00
Beilstein:
1907693
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
crystals
bp
~253 °C (lit.)
mp
65-67 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Oc1ccc(Cl)c(Cl)c1
InChI
1S/C6H4Cl2O/c7-5-2-1-4(9)3-6(5)8/h1-3,9H
InChI key
WDNBURPWRNALGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
3,4-Dichlorophenol (3,4-DCP) is used in the synthesis of (Z)-5-arylmethylidene rhodanines as anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) agent. It can also be used in the preparation of 2-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)-N-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)acetamide for the treatment of inflammatory pain.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Discovery of 2-(3, 4-dichlorophenoxy)-N-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl) acetamide: A selective ?1 receptor ligand with antinociceptive effect.
Navarrete-Vazquez G, et al.
Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 79(20), 284-293 (2016)
The synthesis and SAR study of phenylalanine-derived (Z)-5-arylmethylidene rhodanines as anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) compounds.
Patel BA, et al.
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 23(20), 5523-5527 (2013)
P Larsson et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 54(7), 1864-1867 (1988-07-01)
The microbial degradation of a number of 14C-labeled, recalcitrant, aromatic pollutants, including trichloroguaiacol and di-, tri-, and pentachlorophenol, was investigated in aquatic model systems in the laboratory. Natural, mixed cultures of microorganisms in the water from a brown-water lake with
F O Bryant et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 57(8), 2293-2301 (1991-08-01)
The reductive dechlorination of pentachlorophenol (PCP) was investigated in anaerobic sediments that contained nonadapted or 2,4- or 3,4-dichlorophenol (DCP)-adapted microbial communities. Adaptation of sediment communities increased the rate of conversion of 2,4- or 3,4-DCP to monochlorophenols (CPs) and eliminated the
J H Carey et al.
Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 62(8), 971-975 (1984-08-01)
The disappearance rates of 2,4- and 3,4-dichlorophenol in a small stream were studied and were shown to be first order with respect to either distance or time of flow. Both chlorophenols disappeared at approximately the same rate with average half-lives
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service