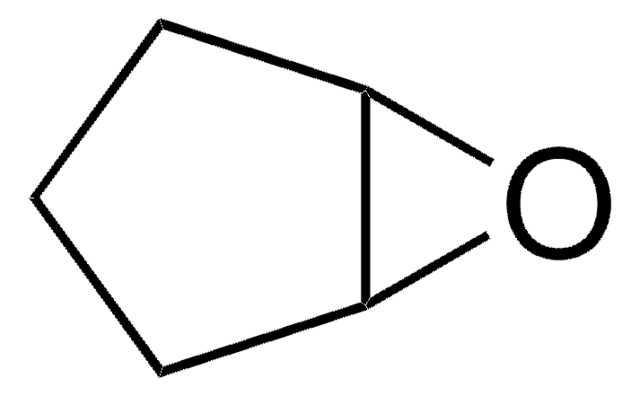
S4921
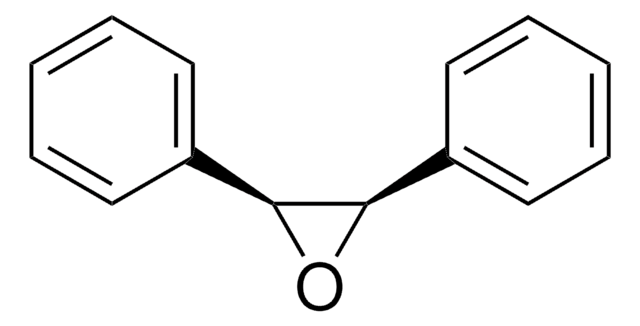
trans-Stilbene oxide
98%
Synonym(s):
trans-1,2-Diphenyloxirane
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C14H12O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
196.24
Beilstein:
82740
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
mp
65-67 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
O1[C@@H]([C@H]1c2ccccc2)c3ccccc3
InChI
1S/C14H12O/c1-3-7-11(8-4-1)13-14(15-13)12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10,13-14H/t13-,14-/m1/s1
InChI key
ARCJQKUWGAZPFX-ZIAGYGMSSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Trans-stilbene oxide also known as trans-1,2-Diphenyloxirane, is often used in photochemistry, whereit can change its structure when exposed to light.Stilbene oxides can break apart when they are excited bylight, leading to the formation of carbonyl ylides. It is also commonlyused to produce trans-stilbene sulfides.
Application
- Chiral Stationary Phases for Liquid Chromatography: Trans-stilbene oxide has been utilized in the fabrication of cellulose derivative-coated spherical covalent organic frameworks, serving as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatographic enantioseparation, demonstrating its pivotal role in advanced analytical methodologies (Yan et al., 2022).
- Method Selection for Chiral High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: Its application extends to the utilization of hysteresis phenomena for chiral high-performance liquid chromatographic method selection in polar organic mode, enhancing the efficiency and specificity of pharmaceutical compound analysis (Horváth et al., 2020).
- Adsorption Properties for Enantioseparations: The effect of chiral selector loading on the adsorption properties of fully- and superficially-porous particles is crucial for high-efficient ultrafast enantioseparations, where trans-stilbene oxide derivatives play a significant role (Felletti et al., 2018).
- Catalysis in Alkene Epoxidation: Trans-stilbene oxide is involved in innovative catalysis research, specifically in the development of carbon nitride-supported Fe(2) cluster catalysts for alkene epoxidation, showcasing its utility in sustainable chemical synthesis (Tian et al., 2018).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Photochemistry of cis-and trans-stilbene oxides
Lee, George A
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 41, 2656-2658 (1976)
Ylva Ivarsson et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1770(9), 1374-1381 (2007-08-11)
Based on the crystal structure of human glutathione transferase M1-1, cysteine residues were introduced in the substrate-binding site of a Cys-free mutant of the enzyme, which were subsequently alkylated with 1-iodoalkanes. By different combinations of site-specific mutations and chemical modifications
Paloma Vidal et al.
The Journal of organic chemistry, 72(9), 3166-3170 (2007-03-10)
This study presents a simple method for measuring long-range heteronuclear coupling constants between protons and proton-bearing carbons. The approach involves recording two conventional 1D-TOCSY experiments in which the offset of the selective proton pulse is set on the low- and
Richard Lonsdale et al.
Biochemistry, 51(8), 1774-1786 (2012-01-28)
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is an enzyme involved in drug metabolism that catalyzes the hydrolysis of epoxides to form their corresponding diols. sEH has a broad substrate range and shows high regio- and enantioselectivity for nucleophilic ring opening by Asp333.
Kouhei Shimomura et al.
Nature chemistry, 6(5), 429-434 (2014-04-24)
In the chromatographic separation of enantiomers the order of elution is determined by the strength of diasteromeric interactions between the components of the mixture and a chiral stationary phase. For analytical purposes, it is ideal to have the minor component
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service