E4143
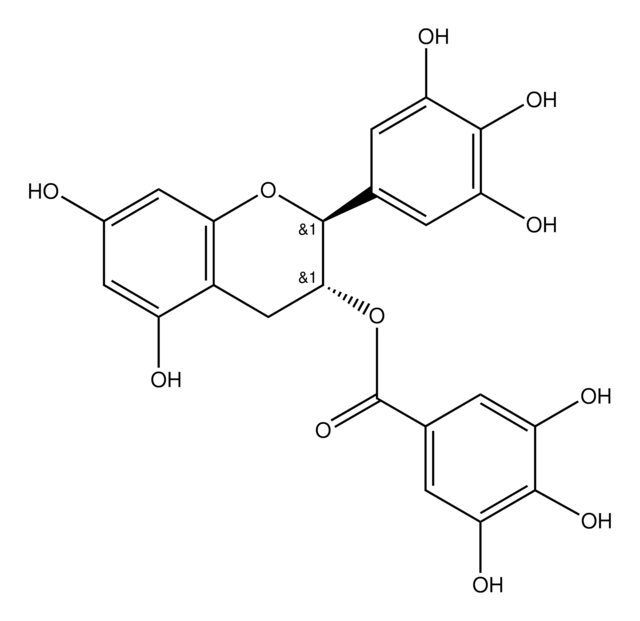
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate
≥95%
Synonym(s):
(−)-cis-2-(3,4,5-Trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-benzopyran-3,5,7-triol 3-gallate, (−)-cis-3,3′,4′,5,5′,7-Hexahydroxy-flavane-3-gallate, EGCG
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95%
solubility
H2O: ≥5 mg/mL, clear
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
Oc1cc(O)c2C[C@@H](OC(=O)c3cc(O)c(O)c(O)c3)[C@H](Oc2c1)c4cc(O)c(O)c(O)c4
InChI
1S/C22H18O11/c23-10-5-12(24)11-7-18(33-22(31)9-3-15(27)20(30)16(28)4-9)21(32-17(11)6-10)8-1-13(25)19(29)14(26)2-8/h1-6,18,21,23-30H,7H2/t18-,21-/m1/s1
InChI key
WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N
Gene Information
human ... CYP1A2(1544)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- as an anti-tumor agent on murine TRAMP metastatic prostate cell line by cell proliferation assay, apoptosis detection and modified Boyden-chamber assay
- induces cell death in acute myeloid leukaemia through death associated protein kinase-2 pathway analyzed through cell viability, cell cycle and apoptosis assay
- as an inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation in murine preosteoclast cell line RAW264.7
- to promote myogenic differentiation
Biochem/physiol Actions
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Chronic inflammation is an underlying factor in the development and progression of many of the chronic diseases of aging, such as arthritis, atherosclerosis, diabetes, and cancer.
Sigma article discusses tumor cell metabolic pathways, focusing on aerobic glycolysis and mitochondrial activity.
Cancer research has revealed that the classical model of carcinogenesis, a three step process consisting of initiation, promotion, and progression, is not complete.
Fatty acid synthesis supports cancer cell proliferation, essential for membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetics.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service