L3295
Phospholipase A1 from Aspergillus oryzae
Synonym(s):
Lecitase™ Ultra, PLA1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in Aspergillus oryzae
form
liquid
specific activity
≥10 KLU/g
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
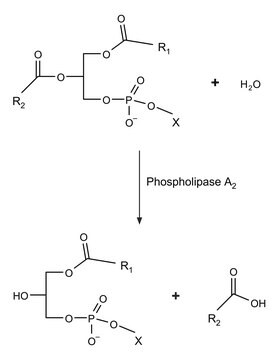
Phospholipase A1 (PLA1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of acyl group from position 1 of lecithin to yield lysolecithin. It is expressed in a wide range of organisms such as rat platelets, bovine brain and testis, hornet venom, bonito muscle and fungi. Gene coding for PLA1 consists of four exons and three short introns spanning 1,056bp of genomic DNA. Mature protein contains 269 aminoacids and two possible N-glycosylation sites (Asn27 and Asn55).
Application
Phospholipase A1 from Aspergillus oryzae has been used:
- in the preparation of sn-1 and sn-2 C18:1- lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) regioisomer standards
- as a catalyst for the synthesis 6-O-glucosyl-poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) in a micro-aqueous system
- to catalyze the synthesis of methyl butanoate and methyl benzoate flavor esters in continuous flow microreactor
- to hydrolyze 17:0 phosphocholine (PC)
Analysis Note
minimum activity 10 KLU/G liquid
Legal Information
Lecitase is a trademark of Novozymes Corp.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Specific enrichment of 2-arachidonoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine in carotid atheroma plaque from type 2 diabetic patients
Menegaut L, et al.
Atherosclerosis, 251(1), 339-347 (2016)
Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase-catalyzed synthesis of natural flavor esters in a continuous flow microreactor
Gumel AM and Annuar MSM
3 Biotech, 6(1), 24-24 (2016)
Jonah E Zarrow et al.
Journal of lipid research, 63(1), 100156-100156 (2021-11-30)
N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE)-hydrolyzing phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) is a zinc metallohydrolase enzyme that converts NAPEs to bioactive N-acyl-ethanolamides. Altered NAPE-PLD activity may contribute to pathogenesis of obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and neurological diseases. Selective measurement of NAPE-PLD activity is challenging, however, because of
Nicole A Housley et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 193(18), 4634-4642 (2011-07-19)
Here we have characterized the Rickettsia prowazekii RP534 protein, a homologue of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoU phospholipase A (PLA) secreted cytotoxin. Our studies showed that purified recombinant RP534 PLA possessed the predicted PLA(2) and lyso-PLA(2) activities based on what has
S G Monic et al.
Scientific reports, 12(1), 4766-4766 (2022-03-21)
Phospholipases are esterases involved in lipid catabolism. In pathogenic micro-organisms (bacteria, fungi, parasites) they often play a critical role in virulence and pathogenicity. A few phospholipases (PL) have been characterised so far at the gene and protein level in unicellular
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service