173401
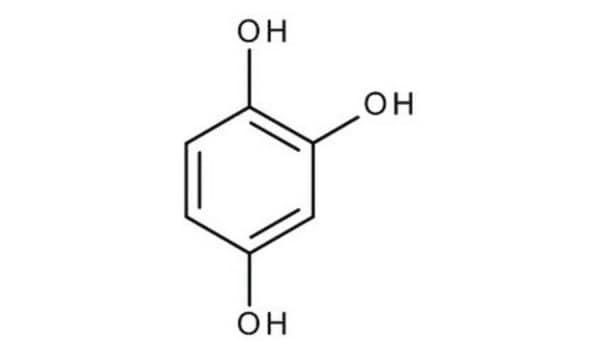
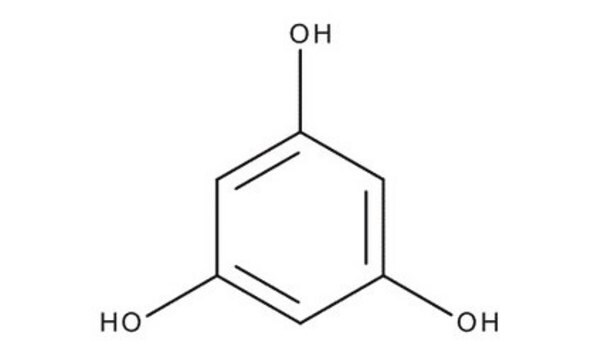
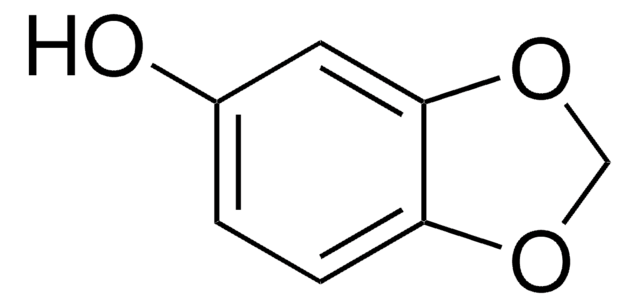
1,2,4-Benzenetriol
ReagentPlus®, 99%
Synonym(s):
Hydroxyhydroquinone
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C6H3(OH)3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
126.11
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
product line
ReagentPlus®
Assay
99%
form
solid
mp
140 °C (subl.) (lit.)
SMILES string
Oc1ccc(O)c(O)c1
InChI
1S/C6H6O3/c7-4-1-2-5(8)6(9)3-4/h1-3,7-9H
InChI key
GGNQRNBDZQJCCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
1,2,4-Benzenetriol is also known as hydroxyhydroquinone. It is an intermediary metabolite of benzene that is present in roasted coffee beans. It is mutagenic and it causes cleaving of DNA single strands by the generation of reactive oxygen species.
Legal Information
ReagentPlus is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Generation of hydrogen peroxide from hydroxyhydroquinone and its inhibition by superoxide dismutase
Hiramoto K, et al.
Journal of Oleo Science, 50(1), 21-28 (2001)
DNA breakage induced by 1, 2, 4-benzenetriol: relative contributions of oxygen-derived active species and transition metal ions
Li AS, et al.
Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 30(9), 943-956 (2001)
Ryuji Ochiai et al.
Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension, 32(11), 969-974 (2009-08-29)
Recent studies suggest that chlorogenic acids, which are the main components of the polyphenol class in coffee, decrease blood pressure, and that hydroxyhydroquinone (HHQ), which is generated by roasting coffee beans, inhibits the antihypertensive effect of chlorogenic acids in brewed
Atsushi Suzuki et al.
American journal of hypertension, 20(5), 508-513 (2007-05-09)
Ferulic acid (FA), a phytochemical constituent, has antihypertensive effects, but a detailed understanding of its effects on vascular function remains unclear. The vasoreactivity of FA was assessed using aortic rings isolated from normotensive Wistar Kyoto (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive rats
Zbigniew Srokol et al.
Carbohydrate research, 339(10), 1717-1726 (2004-06-29)
During the hydrothermal upgrading of biomass, hydrolysis to glucose is an important step. To elucidate some of the reaction pathways that follow this initial hydrolysis, the hydrothermal treatment (340 degrees C, 27.5 MPa, 25-204 s) of dilute (50 mM) solutions
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service