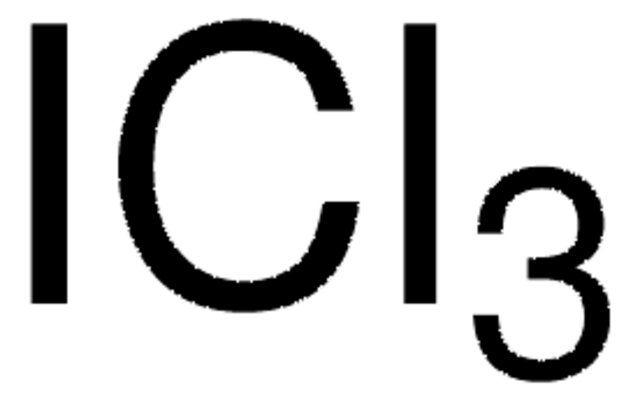714836
Iodine monochloride solution
1 M in acetic acid
Synonym(s):
Chloroiodide solution, Wijs solution
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
ICl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
162.36
Beilstein:
3587194
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352101
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
form
solution
Quality Level
concentration
1 M in acetic acid
density
1.143 g/mL at 25 °C
SMILES string
ClI
InChI
1S/ClI/c1-2
InChI key
QZRGKCOWNLSUDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Iodine monochloride is an inorganic reagent used in the iodination and chloroiodination of aromatic and unsaturated compounds, respectively. It is also used to cleave carbon-metal bonds.
Application
Iodine monochloride can be used:
- As a reagent in the preparation of α-iodo β-ketosulfones from β-ketosulfones.
- In the synthesis of 3-(4-bromo-2-methylphenyl)-4-iodosydnone, which is further used to prepare substituted pyrazoles.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
105.1 °F
Flash Point(C)
40.6 °C
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Synthesis of α-iodo β-ketosulfones and α-iodo methylsulfones using iodine monochloride
Suryakiran N, et al.
Tetrahedron Letters, 47(26), 4319-4323 (2006)
Iodine monochloride
e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. (2013)
Steric effects on the sydnones reactivity. New sydnones and pyrazoles
Dumitracscu F, et al.
ARKIVOC (Gainesville, FL, United States), 2(26), 80-86 (2002)
Zan Qu et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 183(1-3), 132-137 (2010-08-03)
The removal of Hg(0) by the homogenous gas-phase reaction and particle-induced reaction was investigated under various conditions. Iodine monochloride was found to be efficient for Hg(0) oxidation, with the apparent 2nd-order rate constant of about 10.5(±0.3)×10(-17) cm(3) molecules(-1) s(-1) and
K R Siebenlist et al.
Biochemistry, 39(46), 14171-14175 (2000-11-23)
There are conflicting ideas regarding the location of the carboxyl-terminal regions of cross-linked gamma-chain dimers in double-stranded fibrin fibrils. Some investigators believe that the chains are always oriented longitudinally along each fibril strand and traverse the contacting ends of abutting
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service