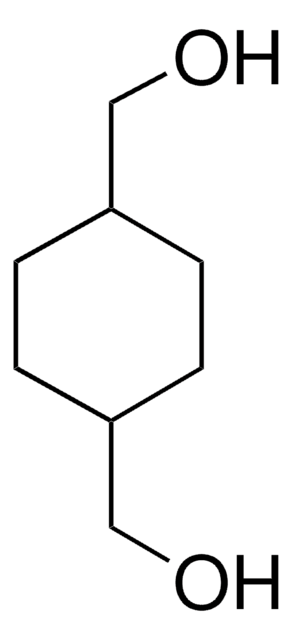
B3000
1,4-Benzenedimethanol
99%
Synonym(s):
p-Phenylene dicarbinol, p-Phenylenedimethanol, p-Xylene-α,α′-diol, p-Xylylene dialcohol, NSC 5097
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C6H4(CH2OH)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
138.16
Beilstein:
2042077
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
powder
bp
138-143 °C/1 mmHg (lit.)
mp
114-118 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
OCc1ccc(CO)cc1
InChI
1S/C8H10O2/c9-5-7-1-2-8(6-10)4-3-7/h1-4,9-10H,5-6H2
InChI key
BWVAOONFBYYRHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
1,4-Benzenedimethanol acts as a chain extender to prepare dimethylsiloxane-urea-urethane copolymers.
Application
1,4-Benzenedimethanol can be used to prepare:
- Poly(6-methyl-ε-caprolactone), which is a key intermediate for the synthesis of polylactide based thermoplastic elastomers.
- A Highly cross-linked polymer named HCP−BDM (hyper cross-linked polymer-1,4-benzenedimethanol) via Friedel−Crafts alkylation in the presence of Lewis acid.
- Sulfonated polynuclear aromatic resins.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Polydimethylsiloxane-urea-urethane copolymers with 1, 4-benzenedimethanol as chain extender
Ho T, et al.
Macromolecules, 26, 7029-7036 (1993)
Synthesis of the sulfonated condensed polynuclear aromatic (S-COPNA) resins as strong protonic acids
Tanemura K, et al.
Tetrahedron, 67(6), 1314-1319 (2011)
Microporous organic polymers synthesized by self-condensation of aromatic hydroxymethyl monomers
Luo Y, et al.
Polym. Chem., 4(4), 1126-1131 (2013)
Polylactide-poly (6-methyl-ε-caprolactone)-polylactide thermoplastic elastomers
Martello MT and Hillmyer M A
Macromolecules, 44(21), 8537-8545 (2011)
Tiejun Ge et al.
Polymers, 11(8) (2019-08-03)
In this experiment, terephthalyl alcohol was used as a modifier to modify phenol under both acidic and alkaline conditions to obtain modified phenols with different molecular structures. Subsequently, the modified phenols reacted with paraformaldehyde in an alkaline environment. After foaming
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service

![1,5,7-Triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/171/446/333d560c-cff6-4958-b489-5acfb3057cce/640/333d560c-cff6-4958-b489-5acfb3057cce.png)