31102
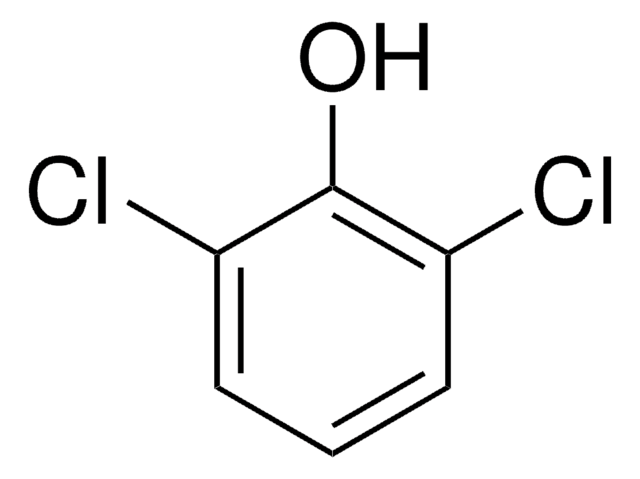
2,6-Dichlorophenol
PESTANAL®, analytical standard
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
analytical standard
product line
PESTANAL®
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
bp
218-220 °C (lit.)
mp
64-66 °C (lit.)
application(s)
agriculture
environmental
format
neat
SMILES string
Oc1c(Cl)cccc1Cl
InChI
1S/C6H4Cl2O/c7-4-2-1-3-5(8)6(4)9/h1-3,9H
InChI key
HOLHYSJJBXSLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- To study the kinetics, performance, and mechanism of the oxidative degradation of 2,6-dichlorophenol (2,6-DCP) by ferrate (VI) (Fe(VI))
- Removal of 2,6-dichlorophenol in water by copper oxide (CuO) activated peroxymonosulfate as catalyst
- Removal of 2,6-dichlorophenol by adsorption with activated polypropylene nanofiber
- Degradation of 2,6-dichlorophenol by Fe-doped titanium oxide(TiO2) sonophotocatalytic process
- Determination of 2,6-dichlorophenol by surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) with molecular imprinting
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service