45688
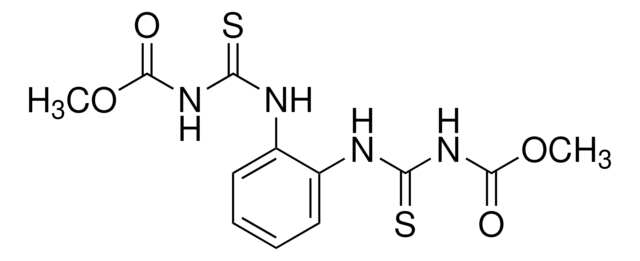
Thiophanate-methyl
PESTANAL®, analytical standard
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
analytical standard
Quality Level
product line
PESTANAL®
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
application(s)
agriculture
cleaning products
cosmetics
environmental
food and beverages
personal care
format
neat
SMILES string
COC(=O)NC(=S)Nc1ccccc1NC(=S)NC(=O)OC
InChI
1S/C12H14N4O4S2/c1-19-11(17)15-9(21)13-7-5-3-4-6-8(7)14-10(22)16-12(18)20-2/h3-6H,1-2H3,(H2,13,15,17,21)(H2,14,16,18,22)
InChI key
QGHREAKMXXNCOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Recommended products
Legal Information
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 2 - Muta. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Chromatograms
application for LC-MS, application for SPEOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service